

Sheeza Basharat6 months ago
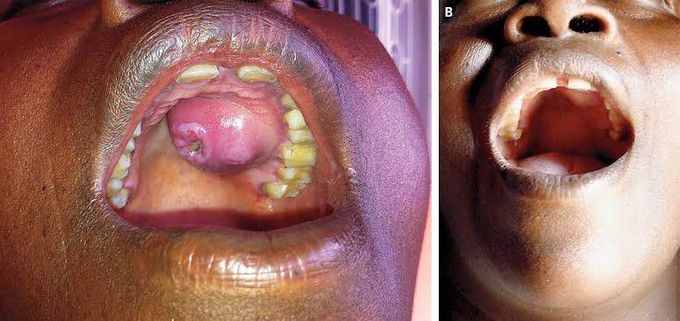
Syphilitic Gumma
A syphilitic gumma is a localized, destructive, tumor-like growth of tissue resulting from tertiary syphilis, a late stage of the Treponema pallidum infection that can occur years after the initial infection. These gummas form as soft, rounded nodules within the skin, bone, organs like the liver, or even the brain. They are caused by an accumulation of dead and swollen fiber-like tissue and are a sign of persistent, untreated syphilis.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Trigeminal NerveChickenpox Vs MeaslesCord ProlapseKey Aspects of Cord ProlapseCord Prolapse- TypesThe Nucleus GigantocellularisFurosemide Dosing ProtocolPeripartum CardiomyopathyBitechchain Review - Is Bitechchain Scam Or legit?Prestigio Marketdex Review - Can Beginners Profit With Prestigio Marketdex? Expert Insights

