
Diffusion weighted MR imaging
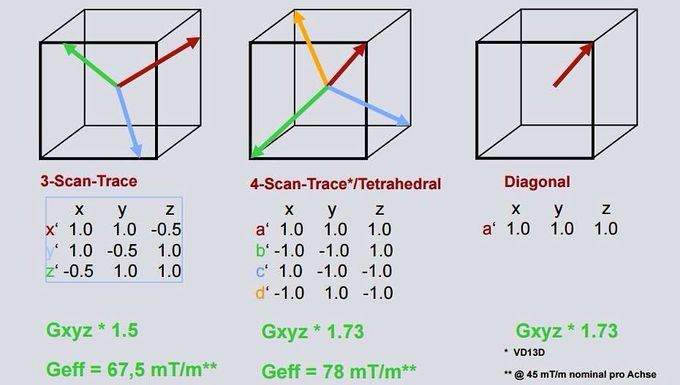
Diffusion weighted MR imaging can be possible by analyzing the spin dephasing and signal loss caused by random motion along magnetic field gradients. The clinical application of the technique has been expanding in the last decade, and is currently used as a routine imaging technique in many hospitals. However, one of the problems with diffusion weighted MR imaging is its relatively lower signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the images especially when using higher b-values. One of solutions for the problem is to use shorter echo time (TE) of the sequence. By using motion probing gradient (MPG) pulses with simultaneous application of all three orthogonal gradients instead of a single orthogonal one, TE could be shortened without reducing the strength of MPG pulses. In this method, four different gradient vectors can be generated, thus it is called tetrahedral technique. It can be used to obtain both isotropic and anisotropic diffusion weighted images.

