
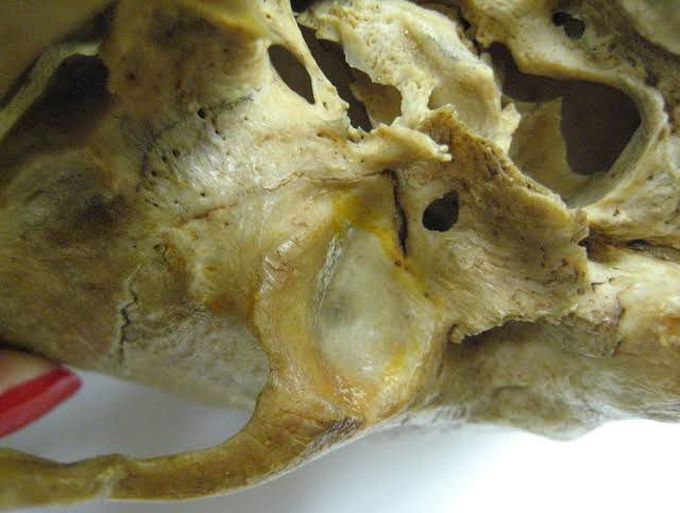
Foramen of Huschke
The foramen tympanicum, or also known as the foramen of Huschke, is an anatomical variation of the tympanic part of the temporal bone in humans resulting from a defect in normal ossification during the first five years of life. Persistence of the foramen tympanicum may also predispose the individual to the spread of infection or tumor from the external auditory canal to the infratemporal fossa or vice versa. It is associated with herniation of soft tissues from the temporomandibular joint into the external auditory meatus, and with formation of fistula between the parotid gland and the external auditory canal. During arthroscopy of the temporomandibular joint, the endoscope may inadvertently pass into the joint via the foramen, with resulting damage

