

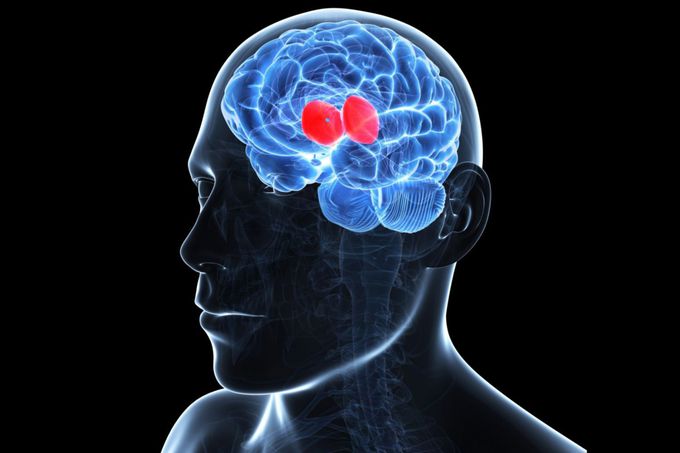
The Thalamus
The thalamus is divided into two walnut-sized parts. Both are found deep in the center of the brain, between the midbrain and the cerebral cortex. The thalamus is a vital structure that has several important functions. There are extensive nerve networks that send signals all around the structures of the brain including the cerebral cortex. The thalamus is involved in sensory and motor signal relay and the regulation of consciousness and sleep. The thalamus may also be involved in the regulation of some types of memory. The thalamus and the cerebral cortex operate in a feedback loop, especially when it comes to the sleep/wake cycle. The thalamus not only sends signals to the cortex, but the cortex in turn sends signals back to the thalamus. Damage to the thalamus can cause coma. The most common forms of injury to the thalamus cause central pain syndrome. This may be caused by bleeding (hemorrhage) when an artery to the brain is blocked. bullet Voluntary Functions bullet Motor Control bullet Consciousness bullet Sleep/Wake Cycle It also regulates the senses of sight, sound, taste, touch and the sense of where the person's body is in space. The thalamus decides which signals from the ears, eyes, mouth and skin to relay to its area in the cerebral cortex.


