

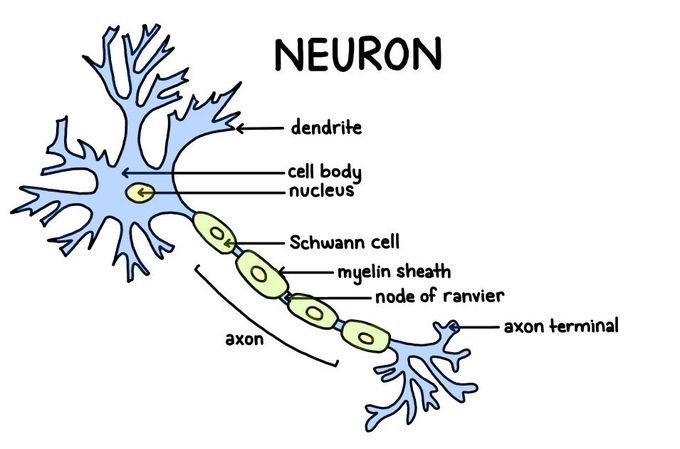
Structure of a neuron
Parts of a neuron Neurons vary in size, shape, and structure depending on their role and location. However, nearly all neurons have three essential parts: a cell body, an axon, and dendrites. Cell body Also known as a soma, the cell body is the core section of the neuron. The cell body contains genetic information, maintains the neuron’s structure, and provides energy to drive activities. Like other cell bodies, a neuron’s soma contains a nucleus and specialized organelles. It’s enclosed by a membrane that both protects it and allows it to interact with its immediate surroundings. Axon An axon is a long, tail-like structure. It joins the cell body at a specialized junction called the axon hillock. Many axons are insulated with a fatty substance called myelin. Myelin helps axons to conduct an electrical signal. Neurons usually have one main axon. Dendrites Dendrites are fibrous roots that branch out from the cell body. Like antennae, dendrites receive and process signals from the axons of other neurons. Neurons can have more than one set of dendrites, known as dendritic trees. How many they have generally depends on their role. For instance, Purkinje cells are a special type of neuron found in a part of the brain called the cerebellum. These cells have highly developed dendritic trees which allow them to receive thousands of signals.

