
Andy Wellsabout 8 years ago
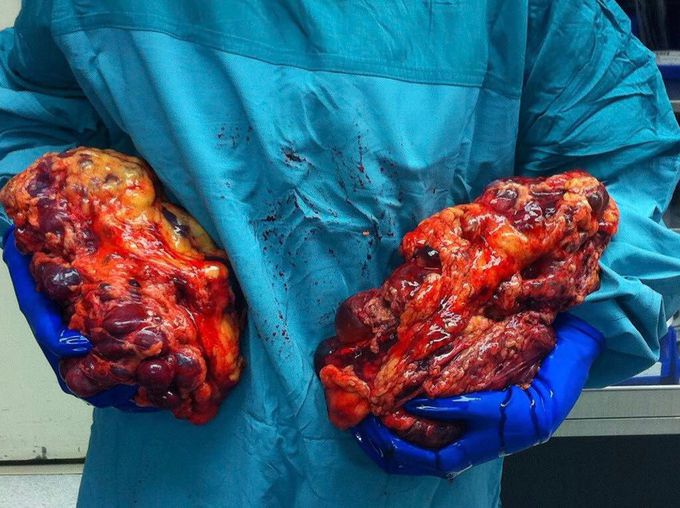
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common inherited renal diseases. It is associated with the progressive development of renal tubular cysts, which replace normal renal tissue. Over time this leads to renal failure in about 50% of sufferers, with these patients requiring dialysis for long-term survival. Studies into the genetic basis of ADPKD have identified two genes that show mutations in ADPKD patients, PKD1 and PKD 2. PKD 1 and PKD 2 encode for two different protein which regulate Ca^2+

