

Fixed Vs Removable prosthesis
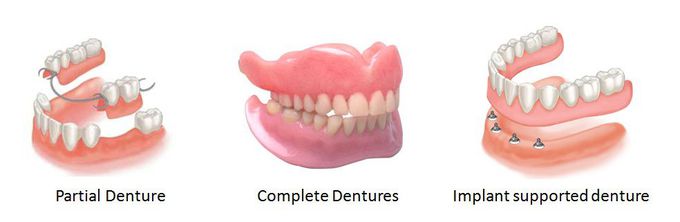
Fixed dental prostheses, like crowns and bridges, are permanently cemented or screwed into place and cannot be removed by the patient, while removable prostheses, like dentures, can be taken out for cleaning. Fixed prostheses offer better stability and chewing function but may be more expensive and require more invasive procedures. Removable prostheses are generally more affordable and easier to clean, but they may not be as stable or comfortable as fixed options. Fixed Prostheses: Definition: Permanently attached to natural teeth or implants, they cannot be removed by the patient. Examples: Crowns, bridges, implant-supported dentures. Advantages: More stable and durable than removable options. Improved chewing function and aesthetics. Can help prevent bone loss and tooth movement. Disadvantages: More expensive and require more invasive procedures. May be more challenging to clean around the edges. Removable Prostheses: Definition: Can be removed and repositioned for cleaning. Examples: Partial or complete dentures. Advantages: More affordable and less invasive to install. Easier to clean by removing them. Can be a good option for patients with limited bone density or gum health. Disadvantages: Less stable and may not be as comfortable as fixed options. May require adjustments over time as the mouth changes.

