

Iqraabout 1 year ago
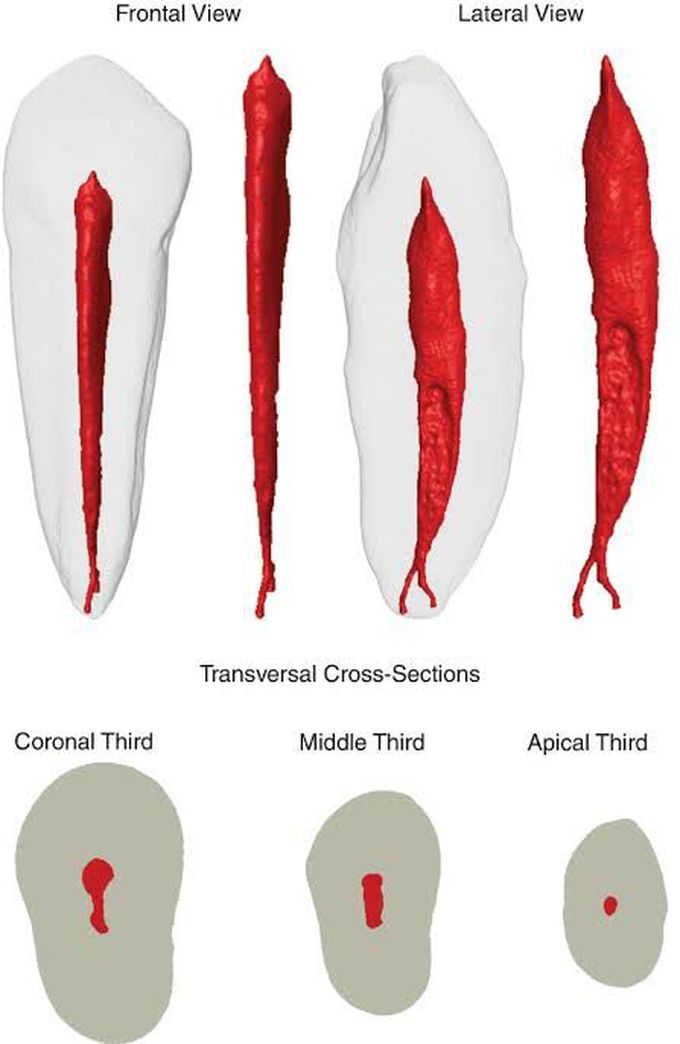
Maxillary canine root
The upper canine root, also known as the maxillary canine root, is characterized by being long, single, conical in shape, and considered the longest root of any tooth in the human mouth; it tapers towards the apex, with a well-developed labial ridge and a prominent cingulum on the palatal surface, and usually has a slight distal inclination; the root cross-section is triangular, with the widest dimension being labio-lingual.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

