

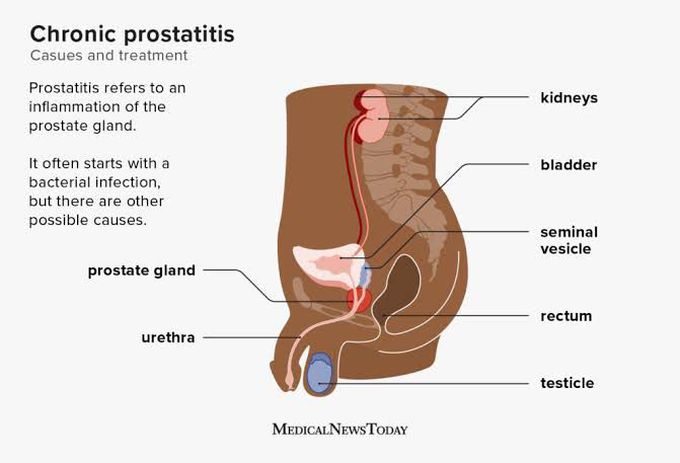
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis evolve from acute Bacterial Prostatitis. Gram negative rods are the most common cause but only one gram positive organisms (enterococcus) is associated with chronic infection. Irritative voiding symptoms,diffuse and poorly localized perineal or suprapubic discomfort are symptoms. On the physical examination of the prostate may feel normal, boggy or indurated. Urinalysis is normal unless secondary cystitis is present. Expressed prostatic secretions demonstrate an increased number of leukocytes. Culture of the secretion or the post prostatic message urine specimen is necessary to make the diagnosis. Trimethoprime-sulfamethoxazole is associated with the best cure rate. The optimal duration of therapy ranging from 6 to 12 weeks.

