

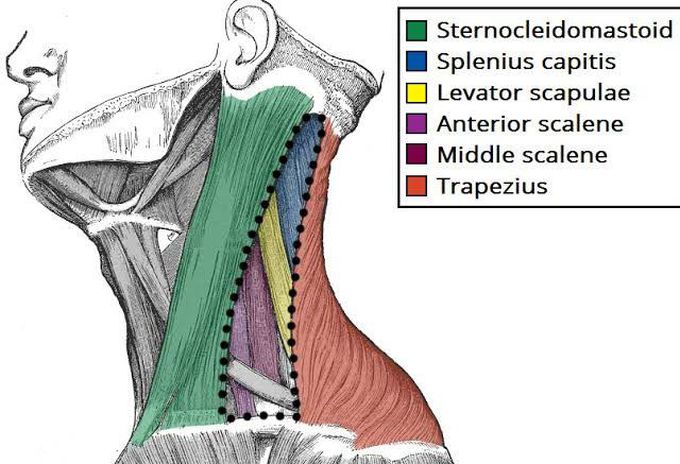
Posterior Triangle of the neck
The most prominent vascular structure of the posterior triangle is the subclavian artery. This artery is found in the subclavian triangle and becomes ensheathed in prevertebral fascia as it crosses deep to the anterior scalene muscle. Directly medial to the anterior scalene, the subclavian artery gives off the thyrocervical trunk, which further branches into the suprascapular, transverse cervical, ascending cervical, and inferior thyroid arteries. The suprascapular and transverse cervical arteries course laterally over the anterior surface of the anterior scalene and supply the muscles of the scapula and the trapezius, respectively. The ascending cervical artery ascends within the prevertebral fascia to supply the deep muscles of the neck. The inferior thyroid artery continues superomedially to the inferior lobe of the thyroid, eventually anastomosing with the superior thyroid artery.[10] There are numerous lymph nodes associated with the posterior triangle that drain local structures and move lymphatic fluid along the chain. The posterior auricular and occipital nodes lie near the apex of the triangle, on the superficial surface of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius tendons. The superficial cervical nodes exist on the anterior aspect of the sternocleidomastoid, while the deep cervical nodes are on the deep surface of the sternocleidomastoid. The posterior cervical nodes accompany the jugular vein as it pierces the investing fascia and enters the posterior triangle. The supraclavicular lymph nodes are on the superior surface of the middle third of the clavicle.[9]

