

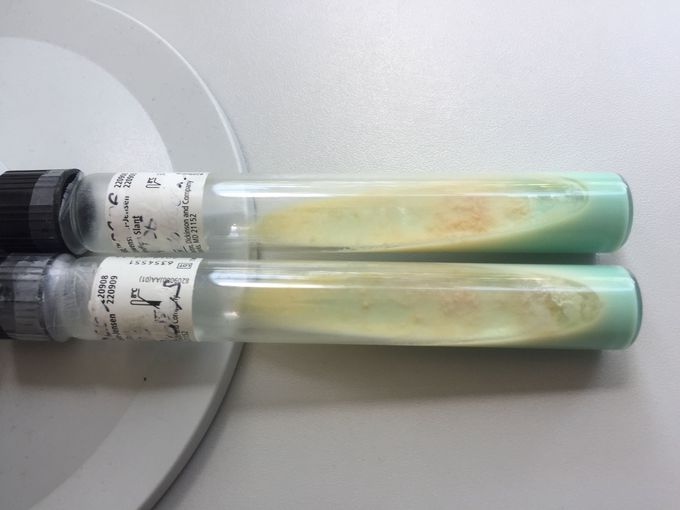
Löwenstein-Jensen Agar with positive M. tuberculosis growth
Löwenstein-Jensen Agar with positive M. tuberculosis growth. When tuberculosis is suspected after X-ray examination and a positive Tuberculin or Interferon Gamma test microbiological tests are required to confirm the diagnosis. No doubt mycobacterium tuberculosis needs special safety measures for culturing. Coughed up sputum, urine, bronchial secretions and other bodily secretions can be used for culturing. Mycobacterium is obligate aerobe and has a lipid-rich cell wall containing mycolic acid. This makes Mycobacterium resistant to disinfectants, detergents, common antibacterial antibiotics and also traditional gram stains. For microscopical identification of this type of acid-fast bacteria Ziehl-Nielson or fluorescent stain is used. You will recognize acid-fast rods but you will not be able to differentiate between various species of Mycobacterium. For definite identification a culture must be grown. Usually Löwenstein-Jensen agar with special safety measures is used. This special medium contains malachite green which gives the tubes a greenish appearance and prevents the culture from being contaminated by other bacteria and fungi acquired through sampling. Coagulated egg and glycerol serve as metabolites. Incubation of culture is required and clear answer will only be possible after 3-4 weeks as M. tuberculosis is a slow growing bacteria. If the evidence of indirect tests (X-ray, tuberculin test, PCR) supports TB diagnosis treatment with antibiotics should be started before culture result. Especially in immunosuppressed patients quick treatment is a matter of life or death.
More than welcome, it's maybe not the most spectacular post but important to know how to work with such specimen and how to diagnose the infection right.


