

Breakthrough in stem cell therapy!
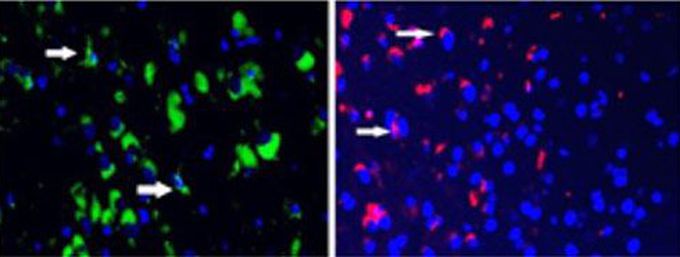
Stem cells are special cells in the body with the ability to differentiate into specific cell types. There are 2 types of stem cells: pluripotent and multipotent. Pluripotent stem cells have the capability to differentiate into any cell type whereas multipotent stem cells can differentiate into only certain cell lines. This ability to be able to differentiate into any cell type is the reason why stem cells are looked towards for the remedy of illnesses and disabilities for which there is presently no cure. Although stem cells, in theory, could be used as a cure, the question remained of how to control the cells in certain locations and to differentiate into the cells we want. Previous studies suggested that stem cells are drawn towards inflammation but using inflammation as a lure can have detrimental effects of its own. Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute have created a drug called SDV1a which is a modified version of an inflammatory molecule CXCL12. In this drug, the inflammation-causing part of CXCL12 has been removed so the drug can successfully lure stem cells to the injected area without causing inflammation. This drug with human neural stem cells (red) has been successfully used in mice with neurodegenerative diseases to significantly slow down the progress of the disease which can be seen from the disappearance of the defective cells (green). Further clinical trials are ongoing but the team is hopeful for its future use. References:- 1. https://www.sbpdiscovery.org/news/worlds-first-drug-guides-stem-cells-to-desired-location-improving-their-ability-to-heal 2. Image taken from the original article.

