

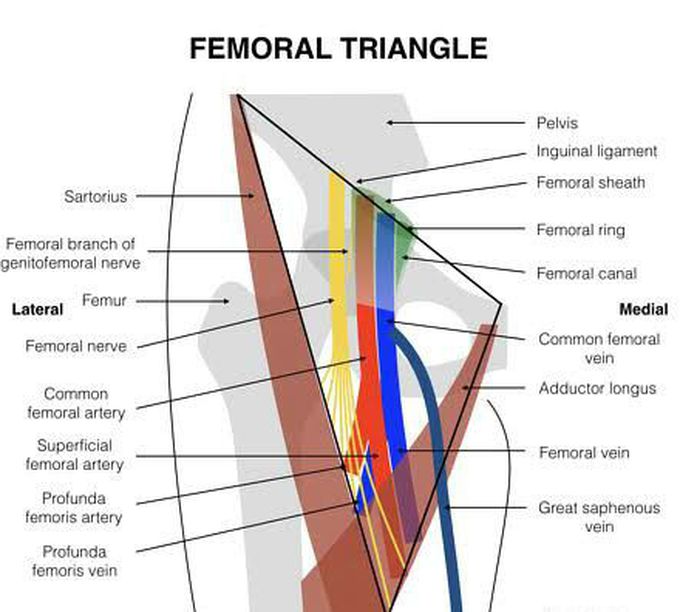
Femoral triangle- boundaries and contents
Femoral triangle (Scarpa's triangle) is a trianglular landmark in the upper third of thigh. It is visible when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated. The femoral triangle is bounded: Superiorly/base- inguinal ligament Medially- lateral border of adductor longus Laterally- sartorius Inferiorly/apex- the point where medial border of sartorius crosses the lateral border of adductor longus Floor- iliopsoas (laterally), pectineus (medially) Roof- fascia lata, cribriform fascia, subcutaneous tissue and skin. Deep to the inguinal ligament is the retro-inguinal space which is divided by the iliopectineal arch- a thickening of iliopsoas fascia, into two compartments. Lateral to the arch is the muscular compartment through which iliopsoas muscle and femoral nerve pass. Vascular compartment is found medial to the arch which contains the major vessels. The contents of the triangle from lateral to medial are (NAVL) : 1.Femoral nerve 2.Femoral sheath and its contents: •Femoral artery •Femoral vein and its proximal tributaries (great saphenous and profunda femoris veins) •Femoral canal which contains lymphatics Image via: https://images.app.goo.gl/asPXtCfotRejhoEh9

