

Management of HIV-Related Ranula Via OK-432 Sclerotherapy
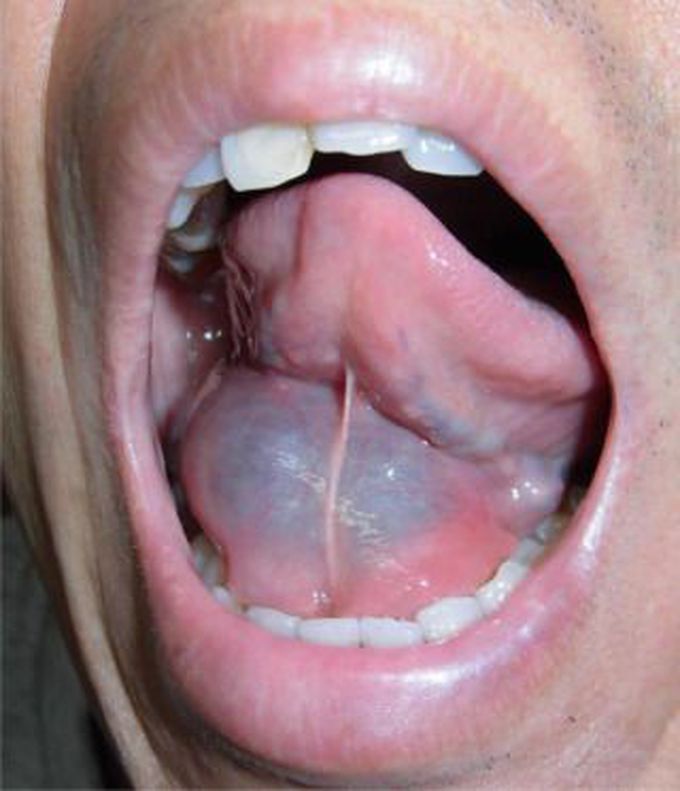
Ranula is a pathology of mouth that presents as saliva filled cyst at the floor of the mouth secondary to blockage of salivary glands. Among various pathologies of head and neck like xerostomia and benign lymphoepithelial cysts in HIV patients, ranula is a common occurrence in the HIV-infected population. An oral ranula typically resolves spontaneously in 6 to 8 weeks. If not resolved, surgery is usually planned for its removal. OK-432 sclerotherapy may also prove beneficial in such cases. OK-432 is a lyophilic mixture of streptococcus pyogenes, which has antineoplastic properties. It is given as an intralesional injection and is an extremely efficacious treatment modality in head and neck pathologies. streptococcus A journal reported a case where 43 years old, HIV positive gentleman, presented with swelling at the floor of the mouth. Medical imaging revealed well-defined lesion at the floor of the mouth, indicative of ranula. OK-432 was chosen as a treatment option die to its minimal invasive technique that ensures safety of the medical personnel treating him. After the aspiration from ranula, which revealed blood-stained mucus, OK-432 solution was then administered intralesional. Patient developed mild complications such as tenderness and inflammation at the site of ranula, and fever; however, these complications resolved spontaneously. Sclerotherapy was repeated again after 3 months. The lesion was resolved completely after 6 months of initiation of treatment. This case report suggests use of OK-432 sclerotherapy as a management option for ranula in HIV-positive patients. Source Treatment of oral ranula in HIV-positive patient https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0385814620300407 Image via https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0385814620300407
Living with HIV was one of the hardest experiences of my life. The fatigue, the emotional toll, and the uncertainty about the future weighed on me every single day. I had tried many treatments and medications, but nothing seemed to restore my health or energy the way I hoped.Out of both hope and desperation, I came across NaturePath Herbal Clinic. At first, I was skeptical but something about their natural approach and the powerful stories I read gave me the courage to try one more time.I began their herbal treatment program, and within a few weeks, I noticed small but meaningful changes more energy, better sleep, and a stronger immune system. Over the months, those improvements only grew. Today, I can truly say my life has changed. I feel healthier, more balanced, and finally in control of my well-being again.This isn’t just a testimony it’s a heartfelt recommendation to anyone living with HIV or any chronic condition. Don’t give up hope. I’m so grateful I gave NaturePath Herbal Clinic a chance. Visit their website to learn more: www.naturepathherbalclinic.com Email: info@naturepathherbalclinic.com
HELLO everyone! Still don’t know the right words to express my Gratitude to the Great DR. Irosi After being diagnosed with the #herpes for the past 1 years, I was given so many health prescriptions and advice with no improvement, I totally lost hope, until I found many testimonies of Great DR. Irosi in an online research Like anybody would be, i advice anyone that is living with herpes can also contact him today, because he has the cure to any virus, disease or illness. Contact him on WhatsApp: https://wa.me/+2349159062807 Email: drirosisolutioncenter@gmail.com
I am Dr. Ayo Christopher, I am a Great traditional Herbal Medicine Doctor. I specialize in treating any kind of diseases and infections using Herbs Medicine. I have the Herbal Cure for Diabetes, Virginal infection, Genital, Gonorrhea, warts virus infections, Leukemia, Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer, Menopause, Hepatitis A B C and HIV and other deadly infections. I have treated more than 20 patients that have Herpes (HSV 2) and all of them were cured. My herbal medicine is 100% safe, there are no side effects and You will start seeing clear results as early as 7 days. If you have been taking conventional medicines for that Herpes infection and you are still having those re-occurring outbreaks, why don’t you try Herbal Medicines and see it get cured in weeks. For more information, send me an Email: ridvid8@gmail.com Telegram: @wafri01 websitehttps: https://ridvid8.wixsite.com/dr-ayo-herbs-home/about-5





