

Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in an Adult
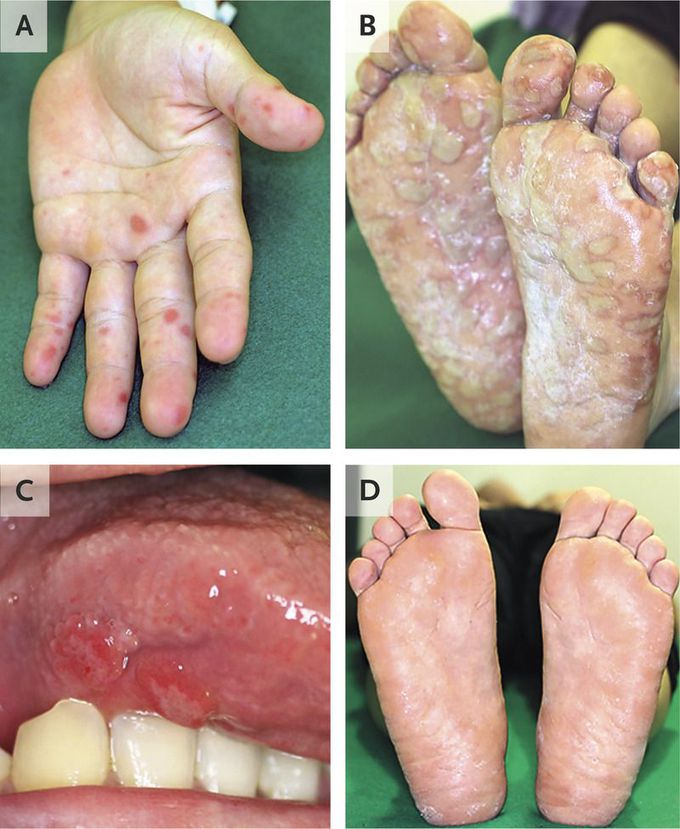
A 36-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with a 5-day history of blisters on his palms (Panel A) and soles (Panel B) and ulcerations on his tongue (Panel C). He also reported fevers, malaise, and a sore throat. One week before his illness began, his 2- and 4-year-old children had had similar symptoms, and they received a diagnosis of hand, foot, and mouth disease. Fluid from a blister on the patient’s right sole was tested by reverse-transcriptase–polymerase-chain-reaction assay, and an enterovirus species was identified; serologic testing for antibodies to coxsackievirus confirmed infection with coxsackievirus A16. Hand, foot, and mouth disease was diagnosed. This disease is caused by enteroviruses and is most common in children younger than 5 years of age. Typically, symptoms are mild and self-limiting, and the diagnosis is made clinically. In rare instances, hand, foot, and mouth disease is associated with severe complications, including meningitis, encephalitis, and myocarditis. The patient’s symptoms abated with supportive care, which included treatment with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication. The lesions on the palms resolved within 2 weeks after presentation. The lesions on the feet (Panel D) and the small ulcerative lesions on the oral mucosa did not resolve completely until 8 weeks after presentation.

