

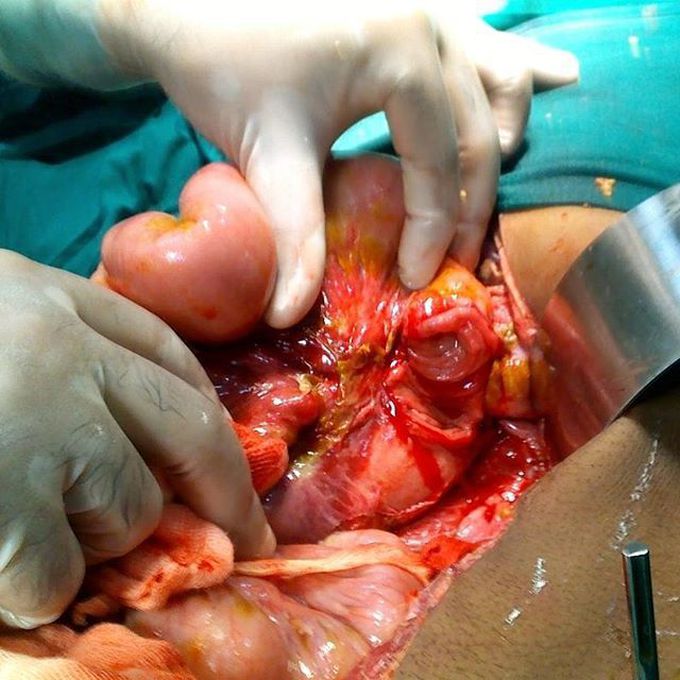
CASE: Blunt trauma to the abdomen with bladder and duodenojejunal flexure rupture.
Bladder injuries can result from blunt, penetrating, or iatrogenic trauma. The probability of bladder injury varies according to the degree of bladder distention; a full bladder is more susceptible to injury than is an empty one. Management varies from conservative approaches that center on maximizing bladder drainage to major surgical procedures aimed at directly repairing the injury.Aside from iatrogenic injuries, patients with signs and symptoms of bladder injury will likely relay a history typical for pelvic trauma. This is fairly straightforward, and generally includes motor vehicle collisions, deceleration injuries, or assaults to the lower abdomen.Clinical signs of bladder injury are relatively nonspecific. Patients often present with the triad of hematuria, suprapubic pain or tenderness, and difficulty urinating or inability to void.

