

HUTCHINSON-GILFORD PROGERIA SYNDROME
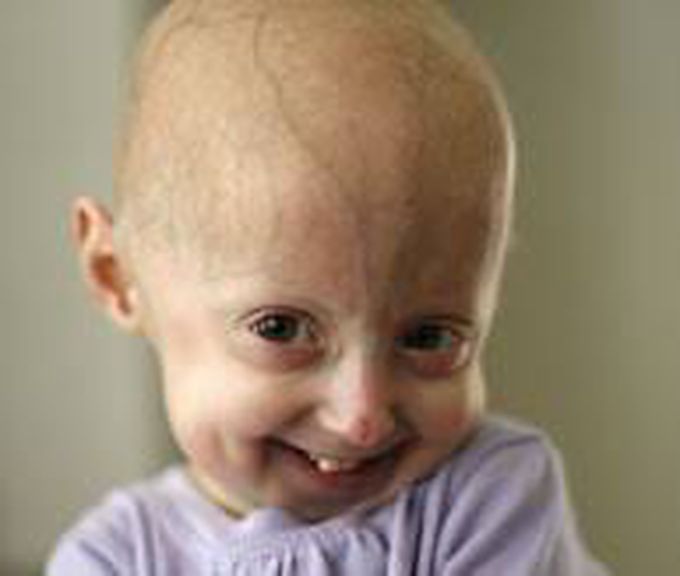
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome is a genetic condition characterized by the dramatic, rapid appearance of aging beginning in childhood. Affected children typically look normal at birth and in early infancy, but then grow more slowly than other children and do not gain weight at the expected rate (failure to thrive). They develop a characteristic facial appearance including prominent eyes, a thin nose with a beaked tip, thin lips, a small chin, and protruding ears. Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome also causes hair loss (alopecia), aged-looking skin, joint abnormalities, and a loss of fat under the skin (subcutaneous fat). This condition does not affect intellectual development or the development of motor skills such as sitting, standing, and walking.People with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome experience severe hardening of the arteries (arteriosclerosis) beginning in childhood. This condition greatly increases the chances of having a heart attack or stroke at a young age. These serious complications can worsen over time and are life-threatening for affected individuals.Progeria is caused by mutations that weaken the structure of the cell nucleus, making normal cell division difficult.Diagnosis is suspected according to signs and symptoms, such as skin changes, abnormal growth, and loss of hair. DIAGNOSIS: A genetic test for LMNA mutations can confirm the diagnosis of progeria. TREATMENT:No treatment has yet proven effective. Most treatment options have focused on reducing complications (such as cardiovascular disease) with coronary artery bypass surgeryand low-dose aspirin. Growth hormone treatment has been attempted.

