

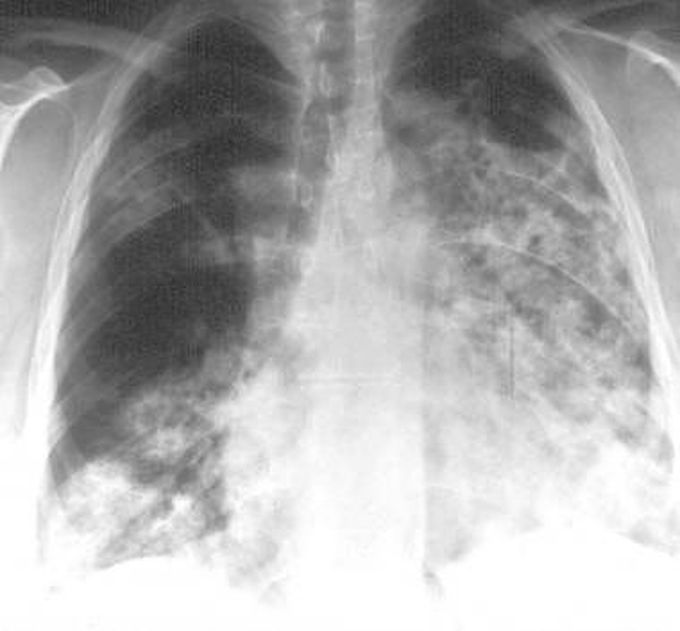
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), formerly known as Wegener's Granulomatosis (WG), is a long-term systemic disorder that involves both granulomatosis and polyangiitis. It is a form of vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels) that affects small- and medium-size vessels in many organs but most commonly affects the upper respiratory tract and the kidneys. Therefore, the signs and symptoms of GPA are highly varied and reflect which organs are supplied by the affected blood vessels. Typical signs and symptoms include nosebleeds, stuffy nose and crustiness of nasal secretions, and inflammation of the uveal layer of the eye. Damage to the heart, lungs and kidneys can be fatal. The cause of GPA is unknown.Geneticshave been found to play a role in GPA though the risk of inheritance appears to be low. GPA treatment depends on the severity of the disease. Severe disease is typically treated with a combination of immunosuppressive medications such as rituximab or cyclophosphamide and high-dose corticosteroids to induce remission and azathioprine, methotrexate, or rituximab to keep the disease in remission. Plasma exchange is also used in severe cases with damage to the lungs, kidneys, or intestines
Can some one describe the radiological findings in this chest x ray , please

