

Zunaira saleh1 day ago
Mandibular infections
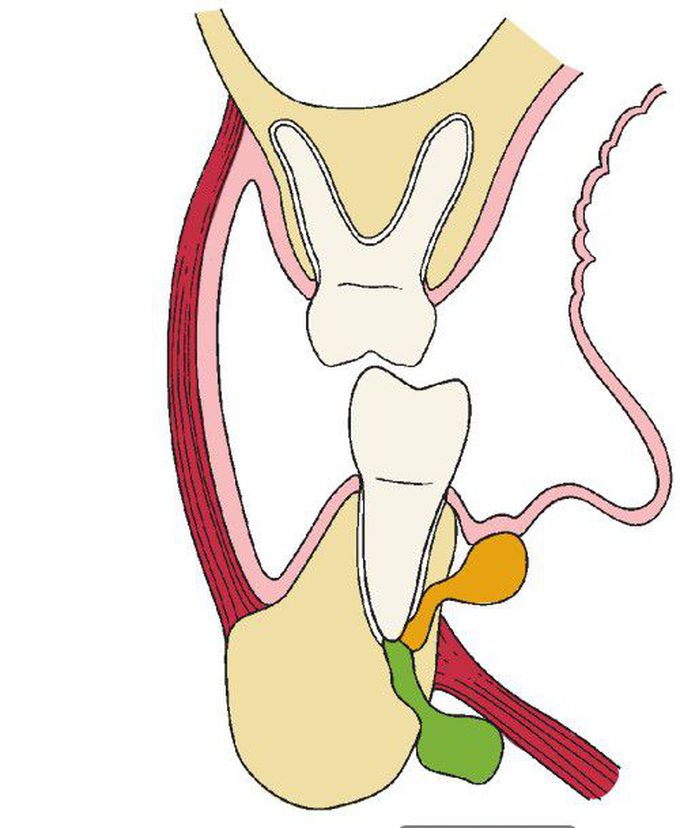
Lingual perforation superior to the mylohyoid attachment will result in involvement of the sublingual space (shown in orange). When the cortical perforation is inferior to the mylohyoid attachment, the submandibular space will be involved (shown in green).
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

