

Zunaira salehabout 1 year ago
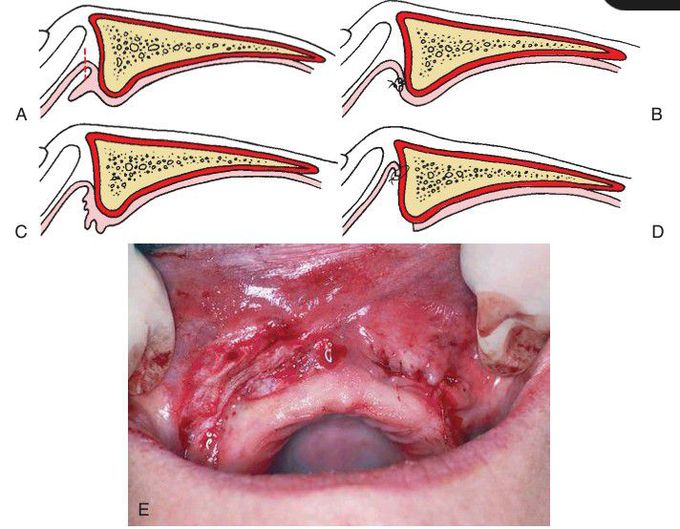
Fibrous hyperplasia
(A) Small, well-localized area of fibrous hyperplasia. This area can be removed with simple excision. (B) Closure of wound margins. (C) Large area of inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia. Removal and primary closure would result in elimination of the labial vestibule. (D) After supraperiosteal removal of excess tissue, the mucosal edge is sutured to the periosteum at the depth of the vestibule. (E) Postoperative view.The smaller well-localized area on the patient’s left has been removed and closed primarily. The larger area of excessive tissue on the right has been removed, and the wound margin has been sutured to the periosteum at the depth of the vestibule, which leaves exposed periosteum.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

