

Dr.Mallick almost 2 years ago
🟢FACIAL NERVE PALSY 🔻
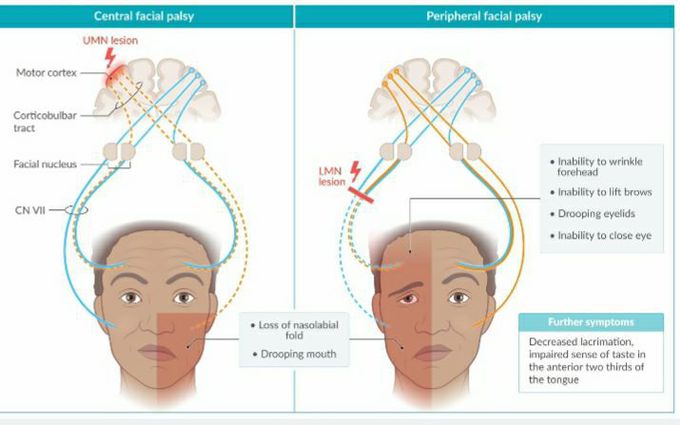
Examination findings in facial nerve palsy. Symptoms in central facial palsy are caused by a contralateral upper motor neuron (UMN) lesion. Because muscles responsible for eyelid and forehead movements are innervated by upper motor neuron fibers from both hemispheres, their function is preserved in central facial palsy. In peripheral facial palsy, damage to lower motor neuron (LMN) fibers results in ipsilateral paralysis of all facial muscles. Because sensory and autonomic fibers join the lower motor neuron fibers of the facial nerve in its peripheral course, peripheral facial palsies can also manifest with non-motoric symptoms.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

