

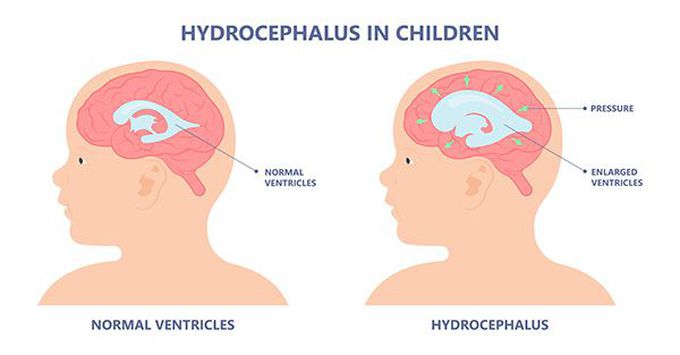
How is hydrocephalus diagnosed
Once a type of hydrocephalus is suspected by a primary physician, one or more of the following tests are usually recommended to confirm the diagnosis and assess the person’s candidacy for shunt treatment. It is important that at this point a neurosurgeon and/or neurologist become part of the medical team. Their involvement is helpful not only in interpreting test results and selecting likely candidates for shunting, but also in discussing the actual surgery and follow-up care as well as expectations and risks of surgery. Clinical Exams – consists of an interview and or a physical/neurologic examination Brain images to detect enlarged ventricles MRI CT or CAT scan CSF tests to predict shunt responsiveness and/or determine shunt pressure Lumbar or spinal tap – large volume External lumbar drainage Measurement of CSF outflow resistance
Women’s Reproductive Health & Daily WellnessGelatine Sculpt | Official WebsiteBurnSlim Official | Support Your Weight Management Journey

