

Iqra7 months ago
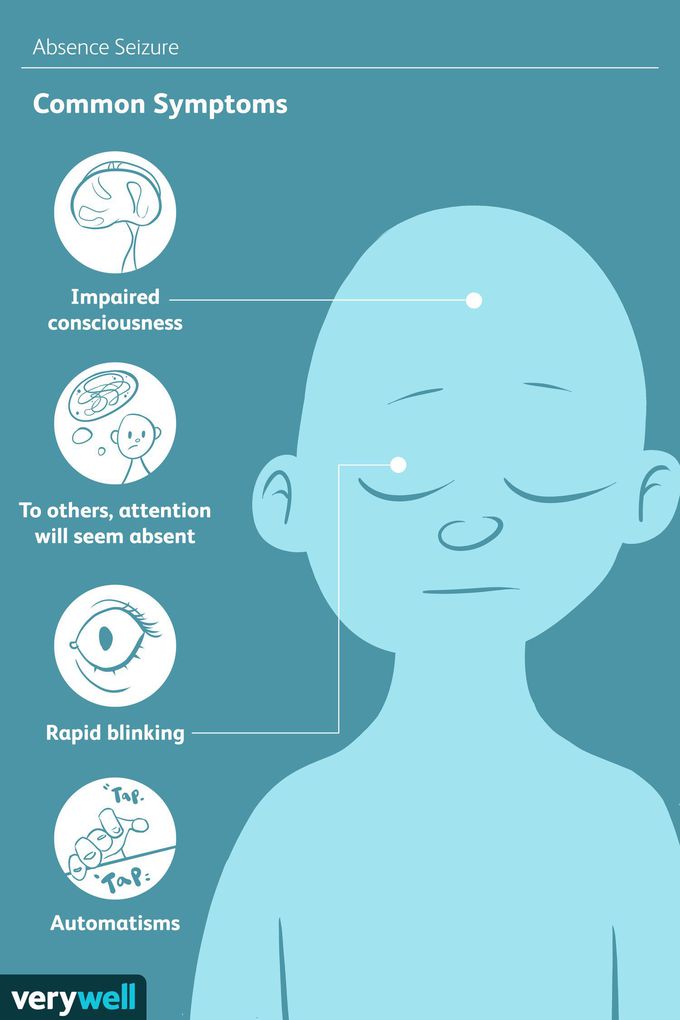
Absence seizures
Absence seizures involve brief, sudden lapses of consciousness. They're more common in children than in adults. A person having an absence seizure may stare blankly into space for a few seconds. Then the person typically returns quickly to being alert. This type of seizure usually doesn't lead to physical injury. But injury can happen if someone is driving a car or riding a bike when the seizure happens. Absence seizures usually can be managed with antiseizure medicines. Some children who have them also develop other seizures, such as generalized tonic-clonic seizures or myoclonic seizures. Many children outgrow absence seizures in their teens.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
join 3rd International Conference on Neurology and Mental Health 2025herniation secondary to raised ICPHyperekplexiaSymptoms of HyperekplexiaDandy Walker Malformation | Diagnosis symptoms and treatment2-Minute Neuroscience: Brain AneurysmsSeizures (Epilepsy) Nursing NCLEX: Tonic-Clonic, Generalized, Focal, SymptomsStroke: Causes, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Prevention | Mass General BrighamNeurofibromatosisSymptoms of absence seizures

