

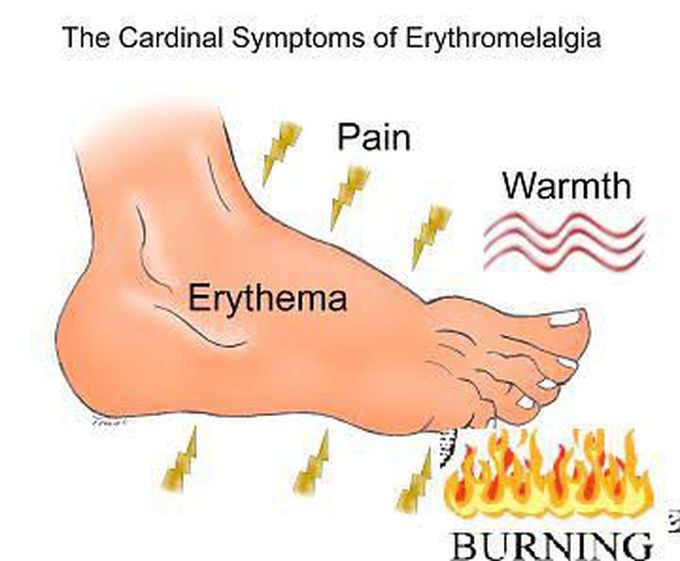
Treatment of burning feet syndrome
Treatment depends on the underlying causes or conditions. Self-care Soak your feet in cool water for at least 15 minutes. This may provide temporary relief. Cold water is not recommended. Avoid exposing your feet to heat. Raise your legs and feet. Take over-the-counter pain medicines (analgesics). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, ketoprofen, or naproxen may temporarily ease pain. Apply topical creams and ointments. Nonprescription creams and ointments containing capsaicin may be applied to the feet to relieve pain. Topical antifungal creams, lotions, sprays, or powders may be used to treat athlete’s foot. Prescription medications Insulin or oral hypoglycemic drugs can control blood glucose levels in people with diabetes. Nutritional supplements may be prescribed for people with vitamin deficiencies. Analgesics. Drugs such as oral or topical narcotic or non-narcotic medications may be prescribed to relieve pain. Topical creams, lotions, Sprays, or patches containing lidocaine may alleviate discomfort. Antidepressants. Tricyclic antidepressants and others may help with chronic pain associated with neuropathy. Anti-seizure or anticonvulsant drugs. Gabapentin, carbamazepine, pregabalin, and others may be used to treat chronic pain. Antifungal drugs. Oral medications may be used for infections resistant to topical products. Physical therapy and exercise Dietary changes Foot pads and shoe inserts (orthotic devices) Surgery. Orthopedic surgery may be necessary in cases that do not respond to medications or more conservative forms of treatment

