

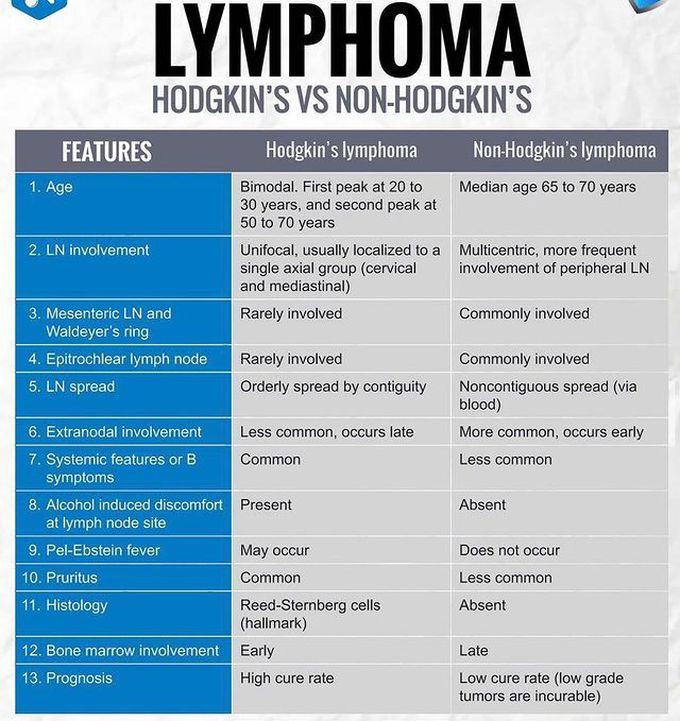
LYMPHOMA
Lymphoma is a general term for cancers that start in the lymph system (the tissues and organs that produce, store, and carry white blood cells that fight infections). The two main kinds of lymphoma are— Hodgkin lymphoma, which spreads in an orderly manner from one group of lymph nodes to another. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which spreads through the lymphatic system in a non-orderly manner. Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma can occur in children, teens, and adults. What Causes Lymphoma? Non-Hodgkin lymphoma becomes more common as people get older. Unlike most cancers, rates of Hodgkin lymphoma are highest among teens and young adults (ages 15 to 39 years) and again among older adults (ages 75 years or older). White people are more likely than Black people to develop non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and men are more likely than women to develop lymphoma. Scientists do not fully understand all of the causes of lymphoma, but research has found many links. For example— Research has shown that people who are infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are at much higher risk of developing lymphoma. Other viruses, such as human T-cell lymphotrophic virus and Epstein Barr virus, also have been linked with certain kinds of lymphoma. People exposed to high levels of ionizing radiation have a higher risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Family history has been linked with a higher risk of Hodgkin lymphoma. Some studies suggest that specific ingredients in herbicides and pesticides may be linked with lymphoma, but scientists don’t know how much is needed to raise the risk of developing lymphoma. Symptoms of Lymphoma Symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma include swollen lymph nodes, especially in the part of the body where the lymphoma starts to grow. Other symptoms include fever, night sweats, feeling tired, and weight loss. These symptoms can also come from other conditions. If you have any of them, talk to your doctor.
Living with HIV was one of the hardest experiences of my life. The fatigue, the emotional toll, and the uncertainty about the future weighed on me every single day. I had tried many treatments and medications, but nothing seemed to restore my health or energy the way I hoped.Out of both hope and desperation, I came across NaturePath Herbal Clinic. At first, I was skeptical but something about their natural approach and the powerful stories I read gave me the courage to try one more time.I began their herbal treatment program, and within a few weeks, I noticed small but meaningful changes more energy, better sleep, and a stronger immune system. Over the months, those improvements only grew. Today, I can truly say my life has changed. I feel healthier, more balanced, and finally in control of my well-being again.This isn’t just a testimony it’s a heartfelt recommendation to anyone living with HIV or any chronic condition. Don’t give up hope. I’m so grateful I gave NaturePath Herbal Clinic a chance. Visit their website to learn more: www.naturepathherbalclinic.com Email: info@naturepathherbalclinic.com


