

Causes of hypoxia
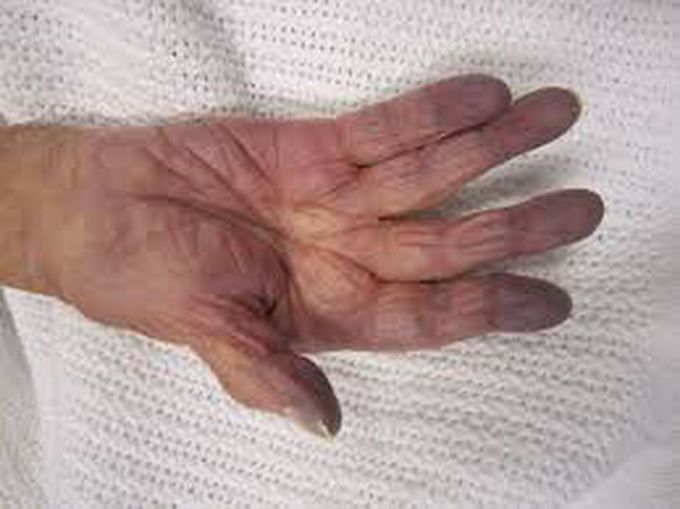
Hypoxia symptoms vary depending on the severity, underlying cause and what parts of your body are affected. When your oxygen is low, you might feel like you can’t breathe or think properly. Some hypoxia symptoms include: Restlessness. Headache. Confusion. Anxiety. Rapid heart rate (tachycardia). Rapid breathing (tachypnea). Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath (dyspnea). Severe hypoxia can cause additional symptoms: Slow heart rate (bradycardia). Extreme restlessness. Bluish skin (cyanosis).The treatment for hypoxia depends on the underlying cause. The cause might be a one-time event or it could be an ongoing condition. Treatments might include: Inhaled steroids that can open up your airways to treat asthma or other lung disease. Medications that help to reduce excess fluid on the lungs (diuretics). Continuous positive airways pressure mask (CPAP) to treat sleep apnea. BiLevel positive airway pressure (often known under the trade name BiPAP®) to treat COPD or and some kinds of sleep apnea. Supplemental oxygen to treat ongoing (chronic) hypoxia. An oxygen delivery device is attached to your nose with a mask or tubes to increase the amount of oxygen getting into your lungs and down to your alveoli. Mechanical ventilation in a hospital, in circumstances of severe acute hypoxia (sudden onset).
I’ve been living with COPD for quite some time, and for years, I struggled to find lasting relief. While conventional medications provided temporary help, the symptoms always returned and often got worse.Out of a mix of hope and hesitation, I decided to try an herbal treatment program from NaturePath Herbal Clinic. I’ll admit, I was skeptical at first. But around the fourth month, I began to notice real, steady progress:My breathing became easier the tightness in my chest lessened my energy levels slowly started to return It wasn’t an overnight transformation, but it was consistent and truly life changing. For the first time in years, I feel more in control of my health. I can breathe more freely, sleep more peacefully, and enjoy daily life without the constant fatigue and breathlessness I once accepted as normal.The improvements I’ve experienced physically, emotionally, and mentally have been nothing short of uplifting.If you’re exploring natural options for managing COPD, I wholeheartedly recommend NaturePath Herbal Clinic. Their approach has made a real difference in my life, and I’m genuinely grateful I gave it a chance.www.naturepathherbalclinic.com info@naturepathherbalclinic.com


