

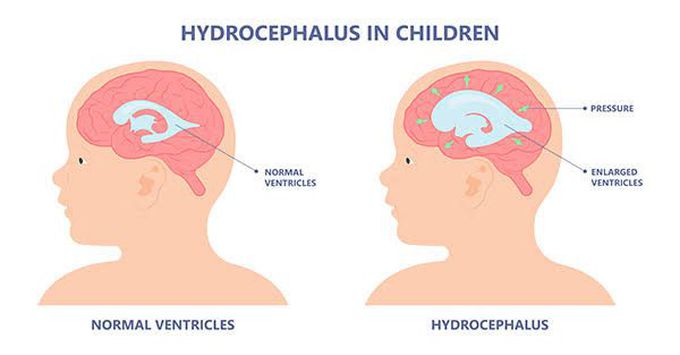
Symptoms of hydrocephalus
The signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus vary somewhat by age of onset. Infants Common signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus in infants include: Changes in the head An unusually large head A rapid increase in the size of the head A bulging or tense soft spot (fontanel) on the top of the head Physical signs and symptoms Nausea and vomiting Sleepiness or sluggishness (lethargy) Irritability Poor eating Seizures Eyes fixed downward (sunsetting of the eyes) Problems with muscle tone and strength Toddlers and older children Among toddlers and older children, signs and symptoms might include: Physical signs and symptoms Headache Blurred or double vision Abnormal eye movements Abnormal enlargement of a toddler's head Sleepiness or sluggishness Nausea or vomiting Unstable balance Poor coordination Poor appetite Loss of bladder control or frequent urination Behavioral and cognitive changes Irritability Change in personality Decline in school performance Delays or problems with previously acquired skills, such as walking or talking Young and middle-aged adults Common signs and symptoms in this age group include: Headache Sluggishness Loss of coordination or balance Loss of bladder control or a frequent urge to urinate Vision problems Decline in memory, concentration and other thinking skills that may affect job performance Older adults Among adults 60 years of age and older, the more common signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus are: Loss of bladder control or a frequent urge to urinate Memory loss Progressive loss of other thinking or reasoning skills Difficulty walking, often described as a shuffling gait or the feeling of the feet being stuck Poor coordination or balance

