

Hunainalmost 3 years ago
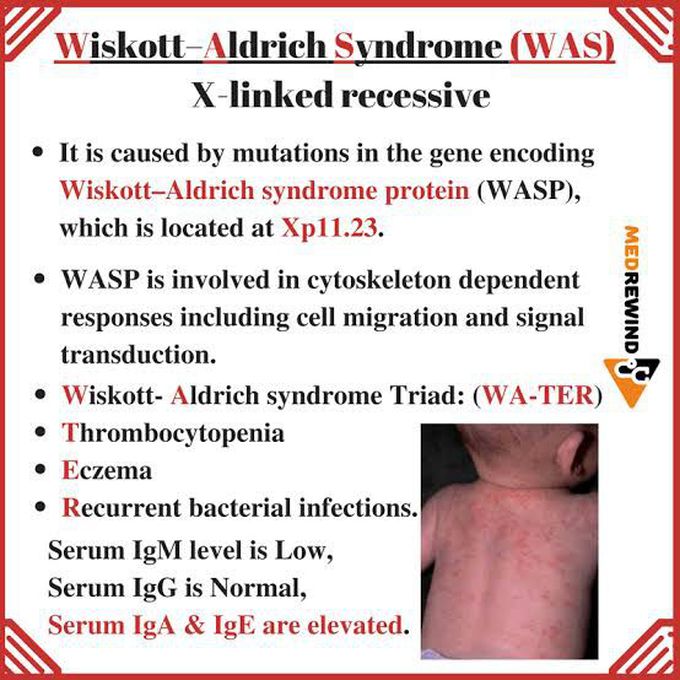
Wiskott aldrich syndrome
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disorder. It usually affects only boys. It results from a mutation in a gene on the X (sex) chromosome (called an X-linked disorder). This gene codes for a protein needed by T cells and B cells (types of white blood cells) to function. Thus, these cells malfunction. B cells do not produce immunoglobulins normally. Platelets (cell particles that help blood clot) are small and malformed. The spleen removes and destroys them, causing the platelet count to be low (thrombocytopenia).
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

