

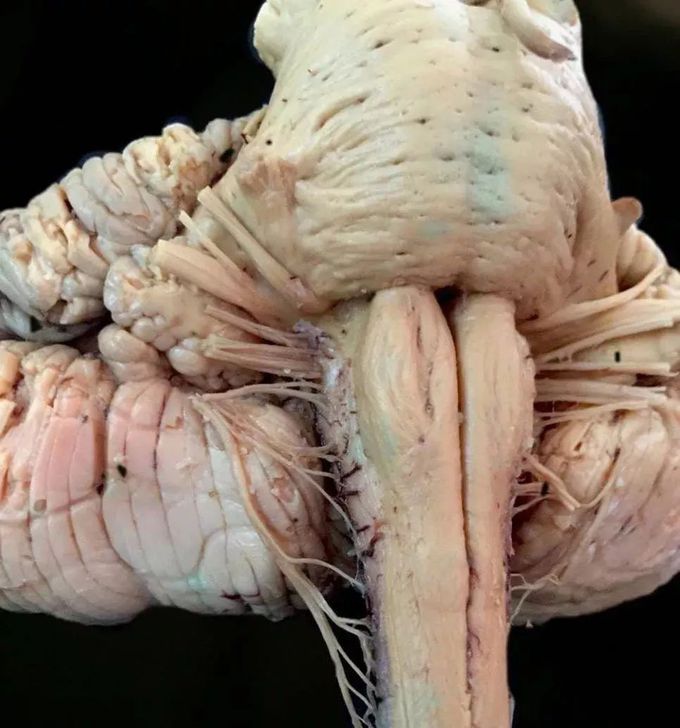
Brainstem
The brainstem is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. The brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem has the critical roles of regulating cardiac, and respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the body back to the brain. These pathways include the corticospinal tract (motor function), the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (fine touch, vibration sensation, and proprioception), and the spinothalamic tract (pain, temperature, itch, and crude touch). The main supply of blood to the brainstem is provided by the basilar arteries and the vertebral arteries. The human brainstem emerges from two of the three primary brain vesicles formed of the neural tube. The mesencephalon is the second of the three primary vesicles, and does not further differentiate into a secondary brain vesicle. This will become the midbrain. The third primary vesicle, the rhombencephalon (hindbrain) will further differentiate into two secondary vesicles, the metencephalon and the myelencephalon. The metencephalon will become the cerebellum and the pons. The more caudal myelencephalon will become the medulla.
Source: https://www.instagram.com/p/CfvqLQws7lx/?igshid=YmMyMTA2M2Y=
