

Hirschsprung Disease
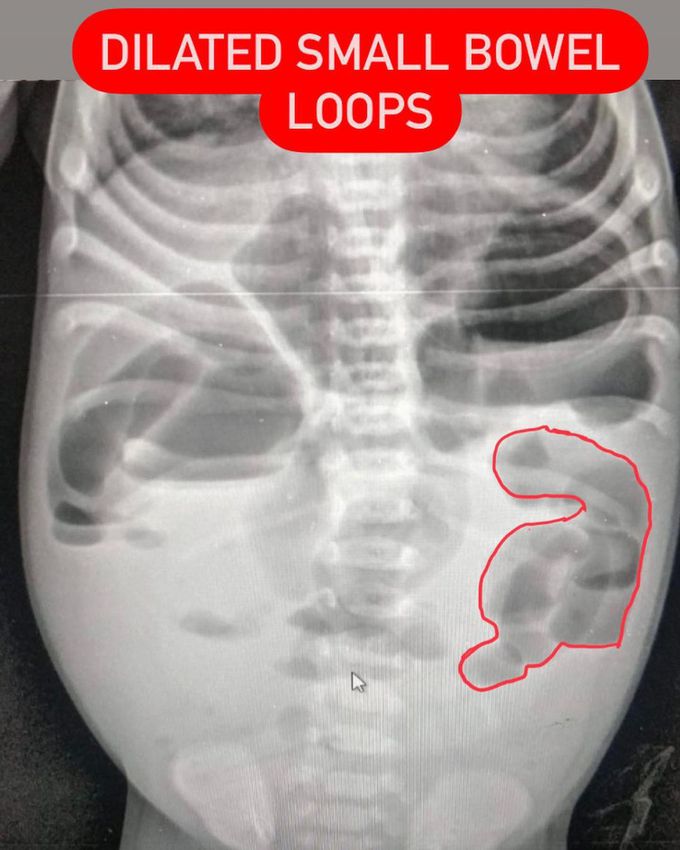
Hirschsprung disease is the most common cause of neonatal colonic obstruction (15-20%). It is commonly characterized by a short segment of colonic aganglionosis affecting term neonates, especially boys. The absence of rectal gas is said to be a sign of Hirschsprung's disease, especially when there is also gaseous distension of the bowel proximally Radiographic features Plain radiograph Findings are primarily those of a bowel obstruction. The affected bowel is of smaller caliber and thus depending on the length of segment affected variable amounts of colonic distension are present. In protracted cases, marked dilatation can develop, which may progress to enterocolitis and perforation. Fluoroscopy A carefully performed contrast enema is indispensable in both the diagnosis of Hirschsprung disease and in assessing the length of bowel involvement. No bowel preperation is needed prior to contrast enema. Barium suspension is made with normal saline to avoid fluid absorption by large surface area of dilated colon. It should be noted, however, that the depicted transition zone on the contrast enema is not accurate at determining the transition between absent and present ganglion cells. The affected segment is of small caliber with proximal dilatation. Fasciculation/saw-tooth irregularity of the aganglionic segment is frequently seen. Additionally, delayed evacuation of the administered contrast medium. Views of particular importance include: early filling views that include rectum and sigmoid colon allowing for rectosigmoid ratio to be determined. transition zone Antenatal ultrasound in particular cases, there may be evidence of fetal colonic dilatation Treatment and prognosis Surgical treatment is by removal of the affected portion of the colon. Where this is successful, the prognosis is good. However, in 3-4% of cases, colonic perforation complicates presentation 2 and this and its sequelae significantly increase both mortality and morbidity. Mortality rates can be as high as 30% due to enterocolitis.
Source: https://www.instagram.com/p/CXEDBnQpB4U/?igshid=YmMyMTA2M2Y=
