
Pawan Nagarover 7 years ago
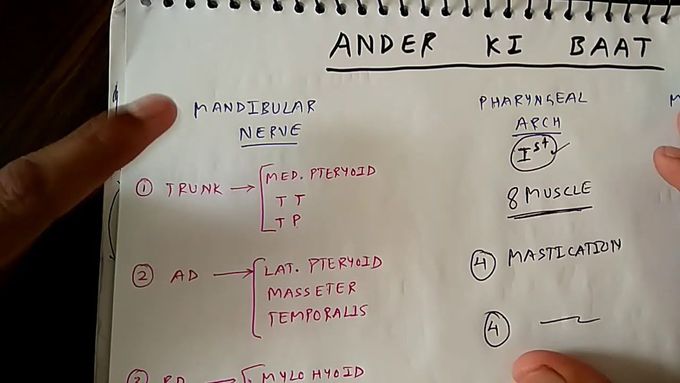
ANDER KI BAAT ( Mandibular nerve , Pharyngeal arch , Maxillary artery )
Mandibular Nerve Pharyngeal Arch ( 1st ) Maxillary Artery ( 2nd part ) Facebook : https://m.facebook.com/story.php?story_fbid=248850155952733&id=144784293025987
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Muscle of mastication and these nerve supplyPharyngeal archesAlterations to pharyngeal arch patterning and homeotic transformations upon perturbation of Hoxa2 expression in mouse embryos. (A) A schematic showing the cNCC Hox code in the pharyngeal arches of the wild-type mouse embryo at pharyngula stage, as in Fig. 1C (see legend for details). (B) Loss of function of Hoxa2 in NCCs results in a homeotic transformation of PA2 to a PA1-like state (depicted as an expansion of the Hoxnegative territory into PA2), and results in a duplicated lower jaw. (C) Conversely, gain of function of Hoxa2 in NCCs results in a homeotic transformation of PA1 into a PA2-like state, resulting in the suppression of jaw formation. (D) Loss of function of the entire HoxA cluster in NCCs leads to partial transformation of PA2-4 to a PA1-like state, leading to a partial quadruplication of the lower jaw. MB, midbrain; PA, pharyngeal arch; r, rhombomere. Sensory nerves of the face (trigeminal nerve, CN V anatomy)Respiratory DiphtheriaMajor blood vessels of the neckMiddle meningeal artery (& extradural haematoma, or why a blow to the side of the head can kill)Submandibular ganglion (and lingual nerve)Pharyngeal arch derivatives.The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves.
The trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve) is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. Its name derives from the fact that each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) has three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions.

