

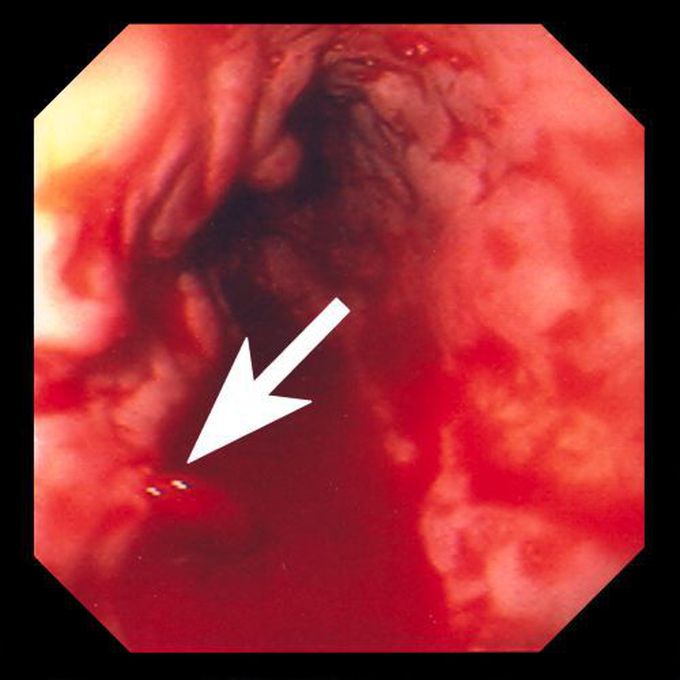
Esophageal Varices on Endoscopy
Esophageal varices develop as a consequence of liver disease that causes back flow of blood into the vessels that are unable to carry large volumes. Esophageal varices are fatal when they leak or rupture. The esophageal varices are asymptomatic. However, when they rupture, the patient presents with: - Vomiting blood - Black stools - Dizziness and lightheadedness - Loss of consciousness Regular surveillance endoscopy is advised for individuals with esophageal varices. In addition, capsule endoscopy is indicated when patient is unable or refuse to get endoscopic exam. Reference: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/esophageal-varices/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351544 Image via: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gastrointestinal-disorders/gastrointestinal-bleeding/varices

