

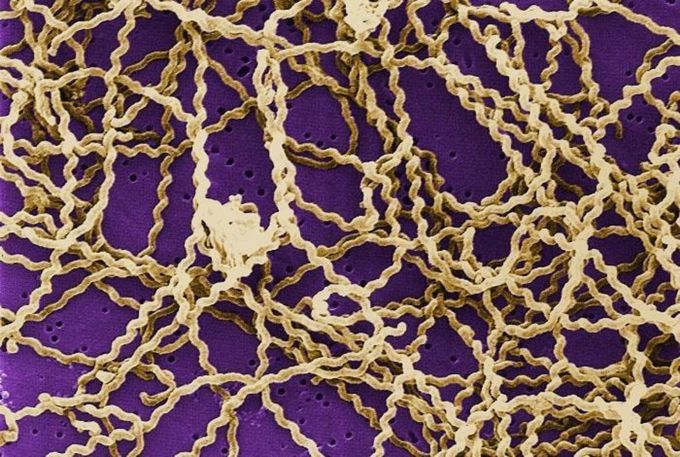
Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is an infectious disease of humans and animals that is caused by pathogenic spirochetes of the genus Leptospira (see the image below). It is considered the most common zoonosis in the world and is associated with rodents in settings of poor sanitation, agricultural occupations, and increasingly "adventure" sports or races involving fresh water, mud, or soil exposure. Leptospirosis is endemic in most areas where dengue virus is transmitted and may be mistaken for dengue, which is typically more common. It is important to consider leptospirosis when dengue is diagnosed in a severely ill patient, because early antibiotics are beneficial in the treatment of leptospirosis and are not given for dengue virus infection. Co-infection occurs in up to 8% of cases.

