

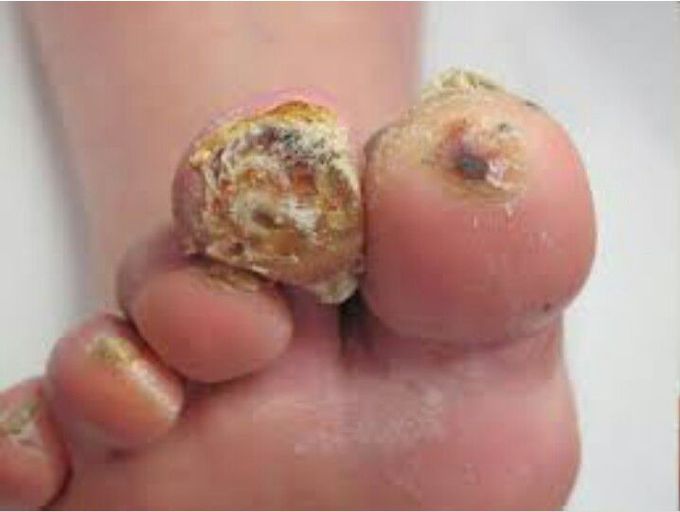
Diabetic Foot Ulcer
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes and is commonly located on the bottom of the foot. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, 6 percent will be hospitalized due to infection or other ulcer-related complication. People who use insulin are at higher risk of developing a foot ulcer, as are patients with diabetes-related kidney, eye, and heart disease. Being overweight and using alcohol and tobacco also play a role in the development of foot ulcers. Pain is usually not a common symptom, but the ulcer is associated with discharge, redness and swelling. To keep the ulcer from becoming infected, keep the glucose lever under normal limits, keep it cleaned and bandaged and clean the wound daily. Appropriate wound management includes the use of dressings and topically-applied medications.

