

Kidney with pheochromocytoma!
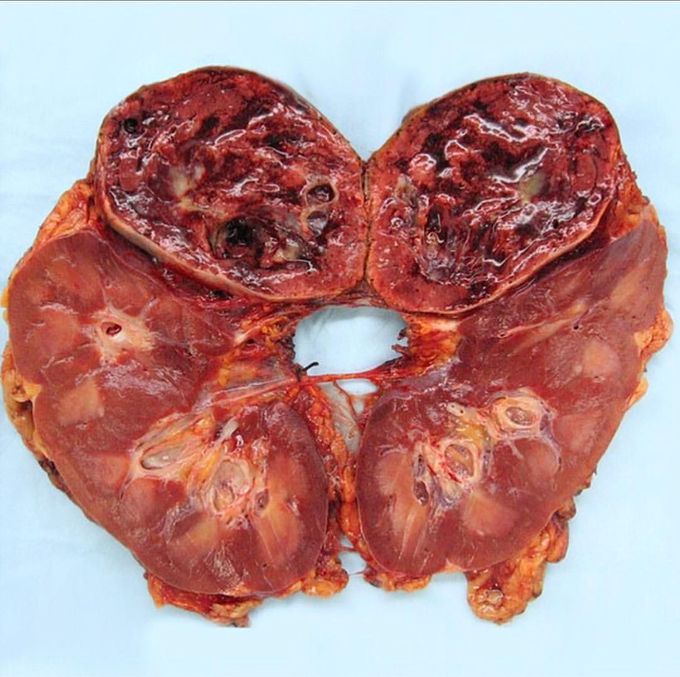
Cross section of a kidney with pheochromocytoma!! This large adrenal neoplasm has been sectioned in half along with the kidney it sits on. Note the grey-tan color of the tumor compared to a small remnant of remaining adrenal at the center. This patient had episodic hypertension and was diagnosed with a tumor arising in the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla - a pheochromocytoma. These are rare tumors that produce, store, and secrete catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine). The condition may be fatal in undiagnosed. Extra-adrenal paragangliomas (described as extra-adrenal pheochromocytomas) are closely related, though less common. The main clinical feature is persistently high and episodic blood pressure (paroxysmal hypertension), severe pounding headache, inappropriate severe sweating, tachycardia, palpitations, and anxiety. MRI and CT scan are used for the diagnosis and tumor localization. Urine screen detects the breakdown products of the catecholamines (metanephrine, vanillylmandelic acid, etc) and plasma metanephrine levels are also useful for diagnosis. Surgical tumor resection with early ligation of venous drainage is the treatment of choice and it usually returns blood pressure to normal and reverses all other symptoms.

