

Ramsha Zaheerover 4 years ago
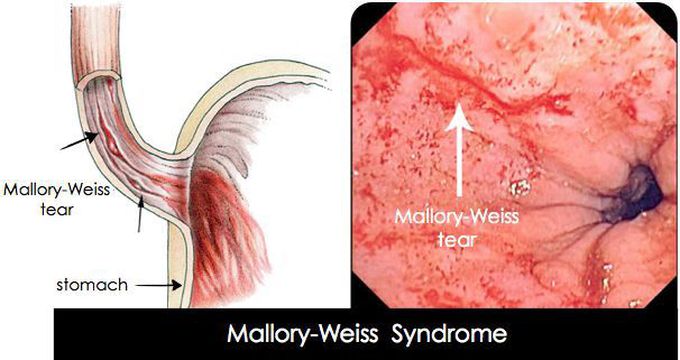
Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
Mallory-Weiss syndrome is characterized by a mucosal tear at or just below the gastroesophageal junction as a result of forceful vomiting or retching. It usually occurs after repeated episodes of vomiting, but may occur even after a single episode. Hematemesis is the most common clinical presentation, varies from streaks of blood in the vomitus to massive bright red blood. It is commonly associated with binge drinking in alcoholics, but any disorder that causes vomiting can induce mucosal tear. Diagnosis is confirmed by upper endoscopy. In most cases, bleeding stops without any treatment but if it continues, angiographic embolization is done.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

