

Ramsha Zaheeralmost 5 years ago
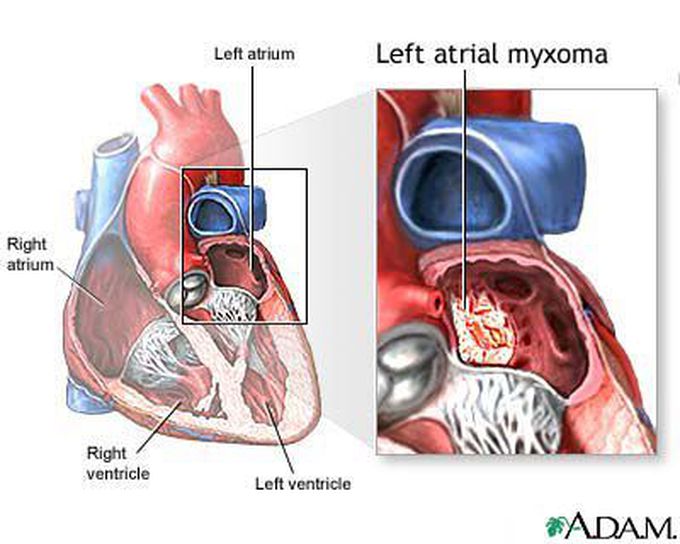
Atrial Myxoma
Atrial myxoma is the most common primary cardiac neoplasm. It is a benign gelatinous outgrowth that is usually pedunculated and arises from the interatrial septum of the heart in the region of the fossa ovalis. Although benign, atrial myxomas can embolize, leading to metastatic disease, or can cause relative valvular dysfunction. It typically presents with fatigue, fever, syncope, palpitations, malaise, and a low-pitched diastolic murmur that changes character with changing body positions. The majority of the atrial myxomas are sporadic, but autosomal dominant transmission has been noted. Treatment includes surgical excision of the tumor.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Melanotic neuroectodermal tumour of infancy.Benign and Malignant Skin LesionsPremature Ventricular Complexes (PVCs)TachycardiaSupraventricular TachycardiaSupraventricular tachycardia- DiagnosisPatent Ductus Arteriosus- SymptomsAtrial Septal Defect- Diagnosis
https://www.facebook.com/AspenDoseCBDGummiesPage/
https://www.facebook.com/AspenDoseCBDGummiesPage/

