

Ramsha Zaheer11 months ago
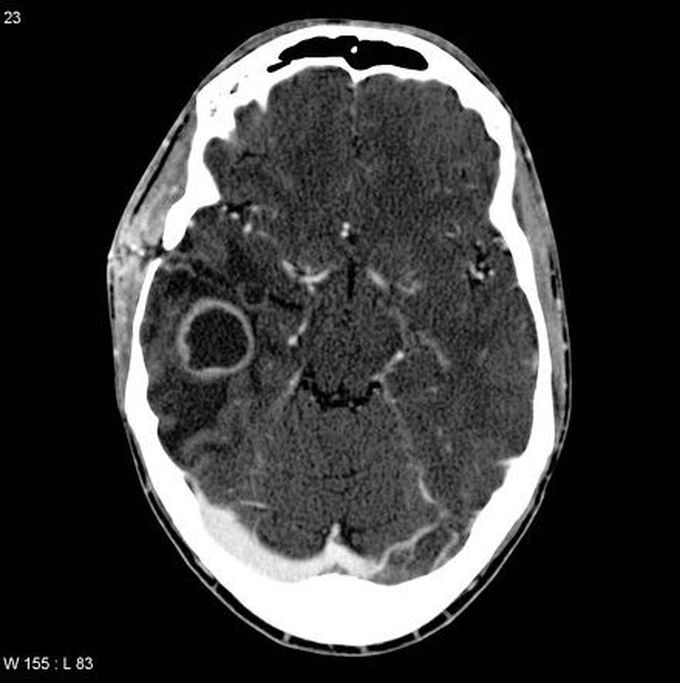
Ring Enhancing Lesion - Brain Abscess!
Brain abscess is a focal suppurative infection of the brain parenchyma commonly caused by streptococci but can be polymicrobial as well. It most commonly affects the frontal lobe, followed by the parietal lobe. Patients commonly present with headache, which is dull and constant in character, focal neurologic deficits, seizures, signs of raised intracranial pressure, and oculomotor and abducens nerve palsy. CT scan is the best initial test for the diagnosis, which shows a ring-enhancing lesion with a low-density core. Treatment is done by intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotics for at least 6-8 weeks.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Dandy Walker Malformation | Diagnosis symptoms and treatment2-Minute Neuroscience: Brain AneurysmsSeizures (Epilepsy) Nursing NCLEX: Tonic-Clonic, Generalized, Focal, SymptomsStroke: Causes, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Prevention | Mass General BrighamExamples of lesions that should be considered for biopsy.NeurofibromatosisAbsence seizuresSymptoms of absence seizuresHow to remember the names of different generations of cephalosporins and their actions against microbes?Leukoplakia

