

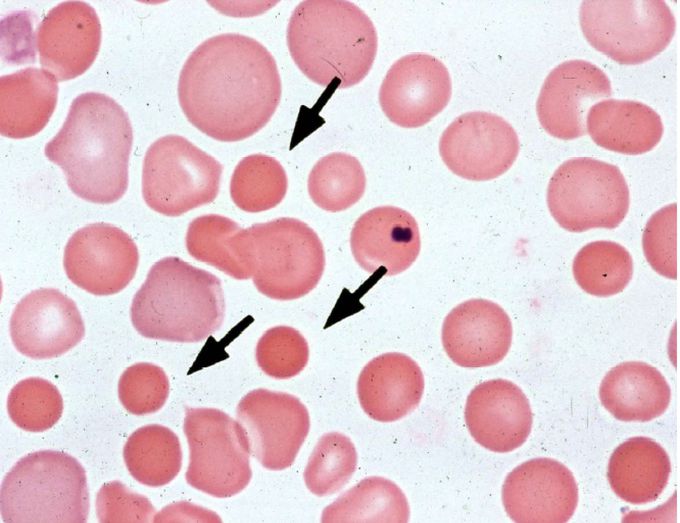
Hereditary Spherocytosis (HS)
Autosomal dominant deficiency in spectrin or ankyrin, an RBC membrane protein resulting in loss of RBC membrane surface area and characteristic biconcave disc. RBCs are forced to spherical shape and gets trapped and destroyed in spleen. Clinically presents as extravascular hemolytic anemia with splenomegaly and jaundice. Acute cholecystitis from pigmented gallstones is a common complication. Best initial test for diagnosis is CBC which shows ⬇️MCV, ⬆️MCHC, and negative Coombs test. A blood smear shows characteristic spherocytes. Most accurate test is Eosin-5 maleimide flow cytometery (replaced osmotic fragility test) and acidified glycerol lysis test. It is manageable by splenectomy to stop hemolysis and chronic folic acid replacement to assist in RBC production. Patient who go through splenectomy are in greater risk of lifelong sepsis and thus require pneumococcal, meningococcal and Haemophilis vaccination before operation.

