

Infectious Mononucleosis (Glandular fever)
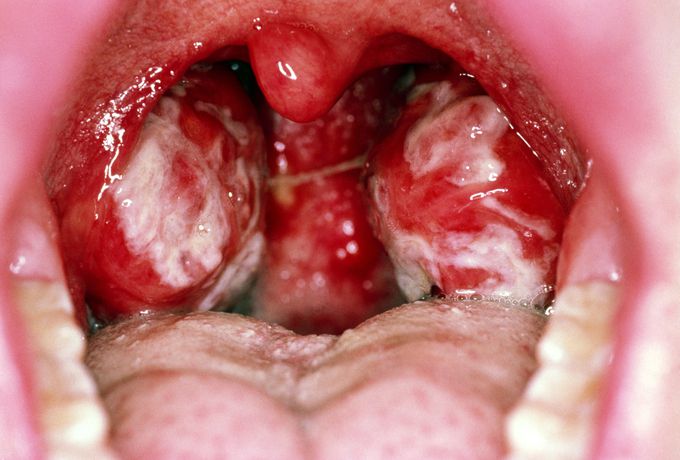
Infectious Mononucleosis or Mono is a group of symptoms caused by Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), a gamma herpes virus. It typically occurs in teenagers or spread through saliva or aerosol, referred to as 'kissing disease'. Clinically patient presents with fever, fatigue and severe pharyngitis. Cervical lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly and antibiotic induced rash(80-90% with ampicillin for sore throat) has also been reported. There are several complications for untreated cases such as airway obstruction due to severe pharyngeal edema as shown in a picture, Splenic rupture or Thrombocytopenia. Several malignancies are also associated with EBV infection such as Nasopharyngeal carcinoma, Burkitt's lymphomas or Hodgkin's disease. There are several diagnostic tools like Monospot test which shows Heterophile antibodies. On a smear atypical lymphocytosis is seen which are activated CD8 T-lymphocytes, also called glandular fever cells but they are non specific findings. Acute infection is characterised by checking for IgM antibodies to viral capsid antigen which is most valuable and specific. Treatment is largely supportive. Steroids can be given in cases of severe pharyngeal edema for five days. Avoiding strenuous activities is advised to reduce risk of splenic rupture until splenomegaly is resolved.

