

Doctors pedia11 months ago
Graves’ Disease
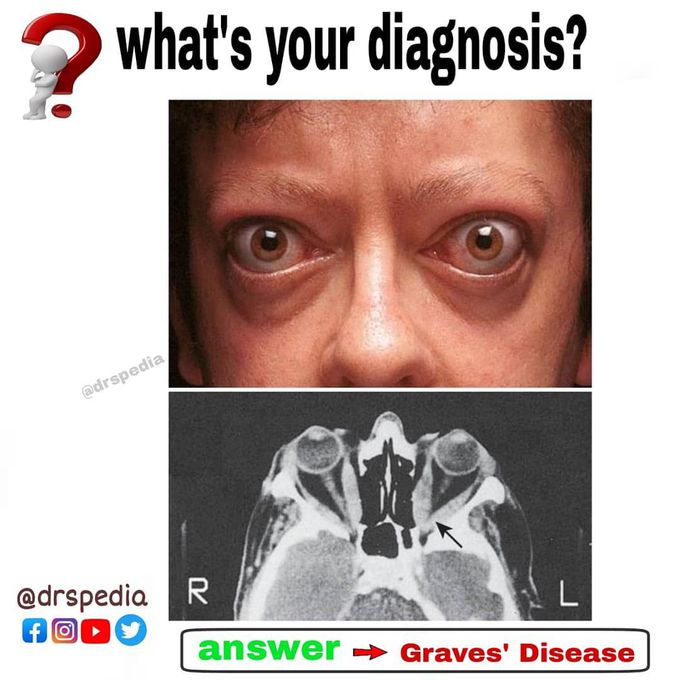
Graves’ disease Bilateral ophthalmopathy with symptoms of diplopia in all directions of gaze and reduced visual acuity in the left eye. The periorbital swelling is due to retrobulbar fat prolapsing into the eyelids, and increased interstitial fluid as a result of raised intraorbital pressure. Transverse CT of the orbits, showing the enlarged extraocular muscles. This is most obvious at the apex of the left orbit (arrow), where compression of the optic nerve caused reduced visual acuity.
Source: https://www.instagram.com/p/CODOoamhOyp/?igshid=oqge7bwidwp0Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

