
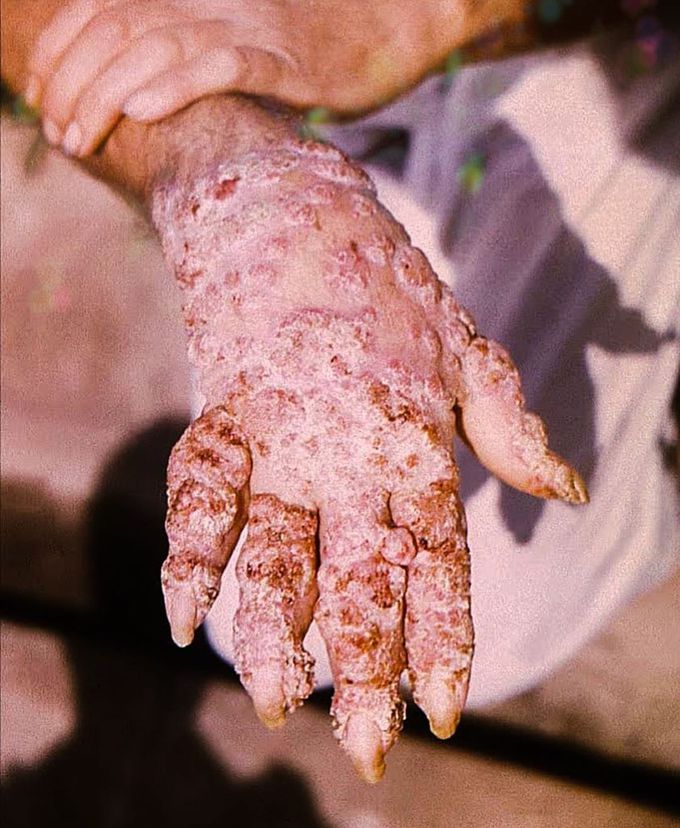
Picture depicting Chromoblastomycosis
Phialophora verrucosa is a pathogenic, dematiaceous fungus that is a common cause of chromoblastomycosis. It has also been reported to cause subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis and mycetoma in very rare cases. In the natural environment, it can be found in rotting wood, soil, wasp nests, and plant debris. Infections caused by P. verrucosa can occur in both immunocompromised individuals, such as individuals who are undergoing immunosuppressive therapies or who have AIDS, as well as in healthy individuals. A healthy individual who became infected with P. verrucosa gained initial exposure through direct contact of the skin with soil containing the fungus. Cases of chromoblastomycosis, subcutaneous phaehyphomycosis, and cutaneous infections caused by P. verrucosa have been reported to present with crusted, warty lesions found on the face, hands, shin, and sole of the foot. Antifungal drugs like itraconazole and terbinafine are typically used to treat infections caused by P. verrucosa.

