

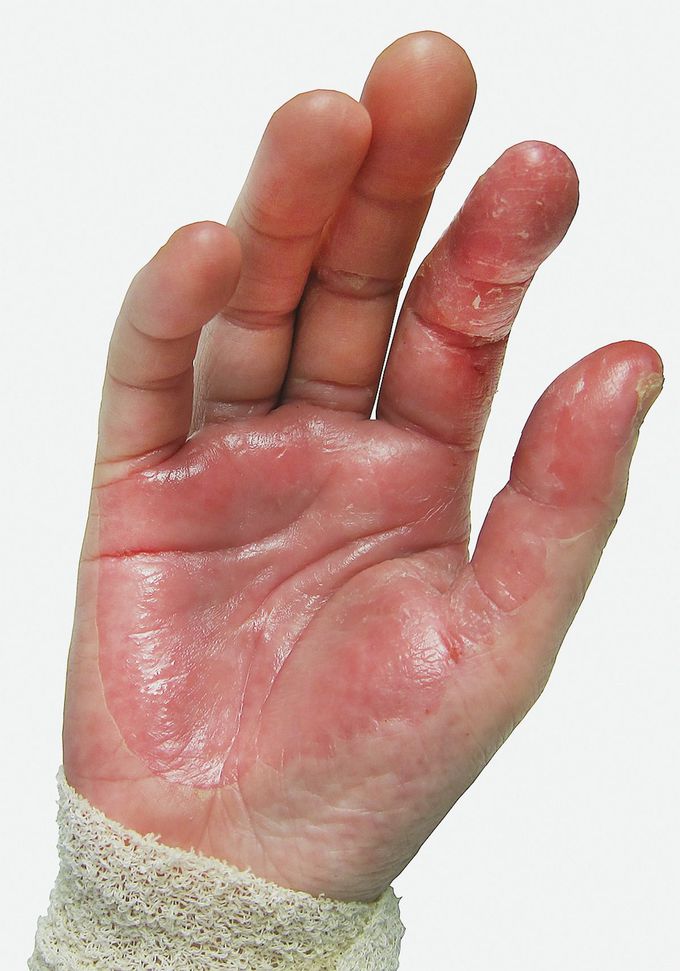
Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome
A 33-year-old woman presented with a 4-day history of fever and abdominal pain, 7 days after undergoing a cesarean section. She had diffuse erythroderma, and the blood pressure was 85/48 mm Hg. A workup revealed elevated creatinine and liver-enzyme levels, and specimens of urine and specimens from the vagina were cultured and grew Staphylococcus aureus. Her condition worsened over the next day, with acute respiratory distress; subsequently, desquamation of her hands occurred. A diagnosis of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome was made. Desquamation is characteristic of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome, typically occurring 1 to 2 weeks after the onset of illness and typically involving the palms and soles. Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome is associated with a wide variety of clinical settings, such as menstruation, postpartum and postsurgical states, barrier contraceptive use, staphylococcal pneumonia, sinusitis, and superinfected skin lesions. With supportive care and the administration of floxacillin, the patient recovered completely. The skin changes resolved within 4 weeks after the onset of illness.
Is floxacillin still working for you nowadays , doctors around the world , it seems that hospitals are encouraging bacteria to become a big monster resistant to all types of antibiotics , always difficult to control what we can't see , especially if a patient took some antibiotic thinking it's for cold or infected skin

