

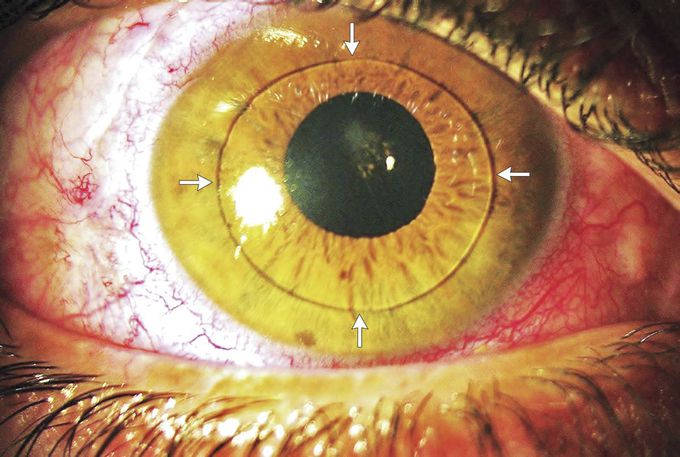
Anterior Dislocation of the Lens
A 30-year-old man presented with sudden, painful vision impairment in his right eye 1 hour after vigorous exercise (long jump). He reported no direct ocular trauma. Slit-lamp examination revealed anterior dislocation of the lens (arrows). Examination of the left eye was unremarkable. The patient underwent surgical extraction of the dislocated lens, anterior vitrectomy, and implantation of an iris-fixated intraocular lens. A workup was performed that included echocardiography, serologic testing for syphilis, and urine chromatography, all of which were unrevealing. Rupture of the zonular fibers (which hold the lens in place) may result in complete dislocation (luxation) or partial dislocation (subluxation) of the lens and could be caused by ocular trauma or other pathologic conditions. Examples of these conditions are intraocular tumors, acquired syphilis and many other conditions that affect the connective tissue (e.g., Marfan's syndrome, homocystinuria, and the Weill–Marchesani syndrome), and spontaneous dislocation of the lens. Surgical removal of the lens is performed to avoid potential complications, such as ocular hypertonia, corneal decompensation, and inflammation.

