

Eagle’s Syndrome
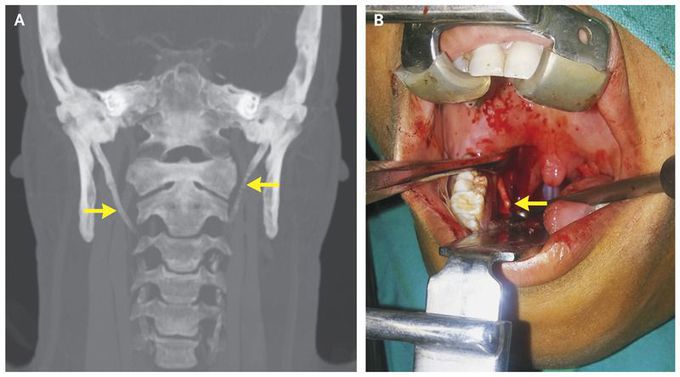
A 35-year-old man presented to the ear, nose, and throat clinic with sharp neck pain and a sensation of having a foreign body in the throat, symptoms that had developed during the past year. At times the pain extended to his right ear. He had no pain or difficulty on swallowing. On physical examination, a bony prominence in the right tonsillar fossa was palpated. Computed tomography revealed two elongated styloid processes that measured 5.5 cm on the right side and 5.2 cm on the left side (reference range, 2.5 to 3.0 cm), with ossification of the stylohyoid ligaments (Panel A, arrows). A diagnosis of Eagle’s syndrome was made. Eagle’s syndrome (first described by American otorhinolaryngologist Watt Weems Eagle) is a rare clinical condition that can be associated with a triad of cervical pain, foreign-body sensation in the throat, and dysphagia. It is caused by the elongation of the styloid process or ossification of the stylohyoid ligament. The patient underwent tonsillostyloidectomy. During surgery, an elongated styloid process was visualized (Panel B, arrow) and was removed on each side. The symptoms resolved immediately after surgery. On follow-up 6 months after surgery, the patient remained asymptomatic and pain-free.

