
Muhammed Thasleem k.c over 6 years ago
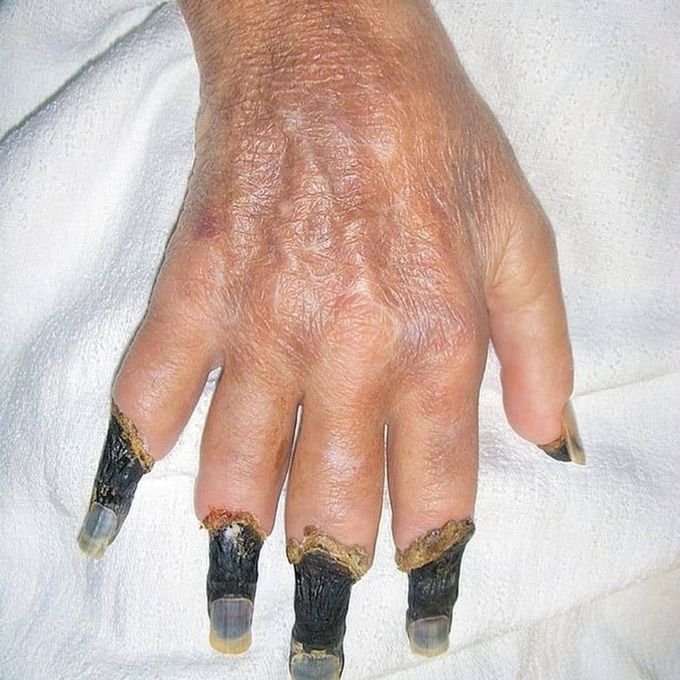
Type II cryoglobulinemia
Cryoglobulinemia is a medical condition in which the blood contains large amounts of pathological cold sensitive antibodies called cryoglobulins – proteins (mostly immunoglobulins themselves) that become insoluble at reduced temperatures. This should be contrasted with cold agglutinins, which cause agglutination of red blood cells. Cryoglobulins typically precipitate (clumps together) at temperatures below normal body temperature – 37 degrees Celsius (99 degrees Fahrenheit) – and will dissolve again if the blood is heated. The precipitated clump can block blood vessels and cause toes and fingers to become gangrenous.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!



