

Adrenal Calcifications in an Infant
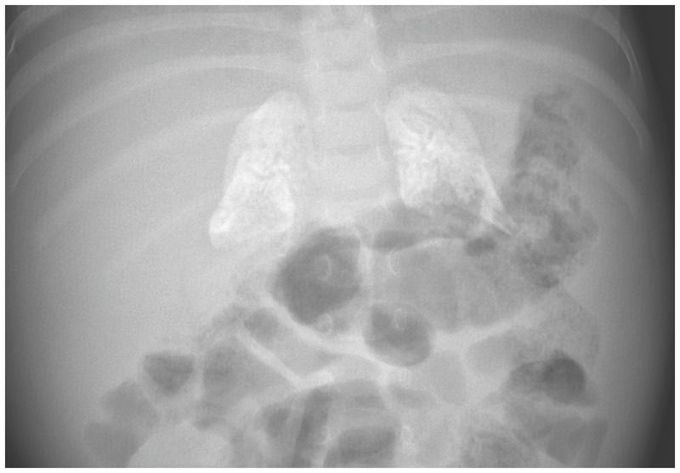
A 4-month-old girl was admitted to the hospital with failure to thrive. After an uncomplicated prenatal course and delivery, she had a normal birth weight of 3350 g. However, at 4 months of age her weight was only 4090 g (z score, −3.5). She was fed a cow’s milk–based formula, and although she had no diarrhea or vomiting at the time of admission, diarrhea developed within a few days after admission. The parents had two other daughters, and both were healthy. Physical examination of the infant revealed a protuberant abdomen with an enlarged liver and spleen. Blood tests showed normocytic anemia, elevated levels of liver aminotransferases, and hyperlipidemia. Plain radiography of the abdomen revealed calcification of both adrenal glands. A dried blood-spot test for enzyme activity was performed and indicated lysosomal acid lipase deficiency. A homozygous mutation in LIPAwas identified on gene sequencing, which confirmed the diagnosis of lysosomal acid lipase deficiency, or Wolman’s disease, an autosomal recessive metabolic condition. Because lysosomal acid lipase is critical for the metabolism of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides, a deficiency leads to lipid accumulation in the liver, spleen, and gut, which causes malabsorption and growth failure, and to calcification of the adrenal glands. Genetic counseling was provided, and the infant was treated with recombinant human lysosomal acid lipase. A low-fat formula and parenteral nutrition were provided. The patient’s growth began to improve, and at 9 months of age she weighed 6500 g (z score, 2.6). Her development is steadily improving, but psychomotor delay is still present.

