

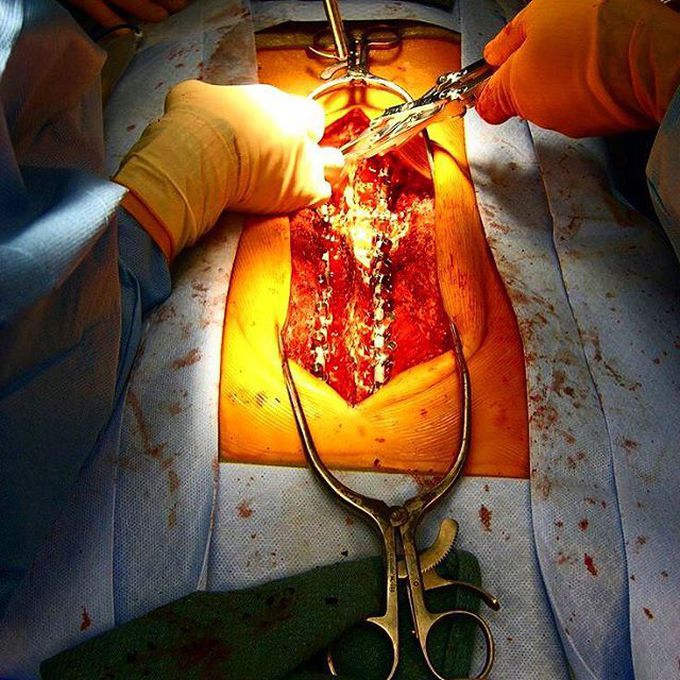
A cool intraoperative picture showing a surgical correction for scoliosis!!!
An abnormal lateral curvature of the spine is a condition called Scoliosis. In all cases, prior corrective surgery, the degree of the spinal deformity is measured by Cobb angle, with scoliosis defined as a lateral spinal curvature with a Cobb angle of 10° or more.Reasons for scoliosis are broad, including congenital (from birth), neuromuscular scoliosis seen in spina bifida and patients with cerebral palsy, degenerative scoliosis due to a trauma, major previous back surgery, or osteoporosis, and idiopathic scoliosis with no apparent reason. The primary goal of surgical treatment is prevention of curve progression. Spinal fusion is the procedure used to correct problems of the spine (vertebrae), such as scoliosis, fractures, and degenerative disk diseases. The basic idea is to fuse together the vertebrae so that they heal into a single, solid bone. Hooks and screws are applied to the spine to anchor long rods, ensuring the correction of the curvature and its stability over time in a way that redistributes the stresses on the bones and keeps them in proper alignment while the bones of the spine fuse. Photo by @paboards
Hemodynamic stimuli&nonhemodynamic stimuliWhat is scoliosis?Effects of sugar on teeth

