

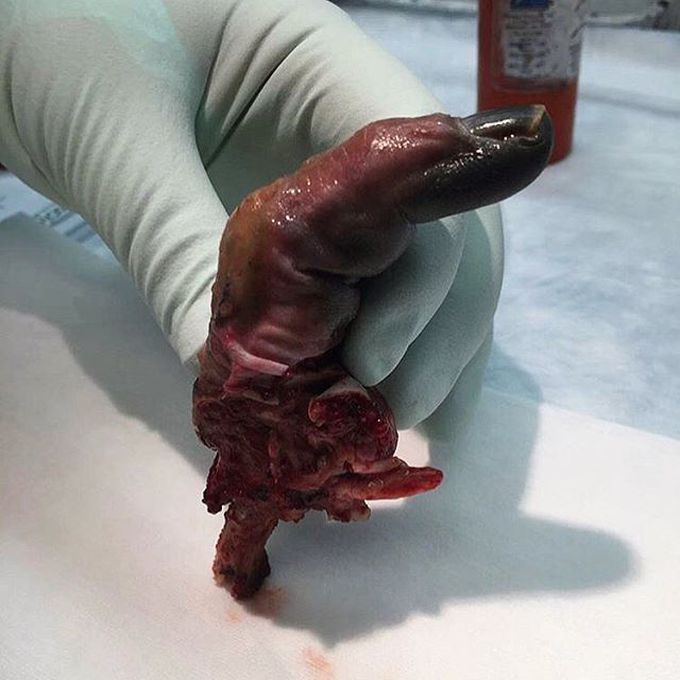
Ischemic finger in a case of a complicated tenosynovitis!
This patient has suffered a MRSA pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis leading to digital ischemic necrosis and amputation. He presented to the emergency department with right index finger pain and swelling a few days after sustaining a puncture wound. As seen in the picture, his finger had a flexed position on presentation and passive extension was painful. Pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis is the infection and inflammation of the synovial sheath that surrounds the flexor tendon of the finger. This is most commonly happens as a result of a penetrating trauma to the tendon sheath or from a direct spread from a septic joint or a deep space infection, with the majority of cases involving staph aureus and MRSA. Diagnosis is mainly clinical, and once diagnosed, surgical intervention is necessary, along with culture-specific IV antibiotics. If the finger can be salvaged, either closed tendon sheath irrigation or open irrigation and debridement (for severe cases) technique with a angiocatheter can be used.
Hemodynamic stimuli&nonhemodynamic stimuliEffects of sugar on teeth

