

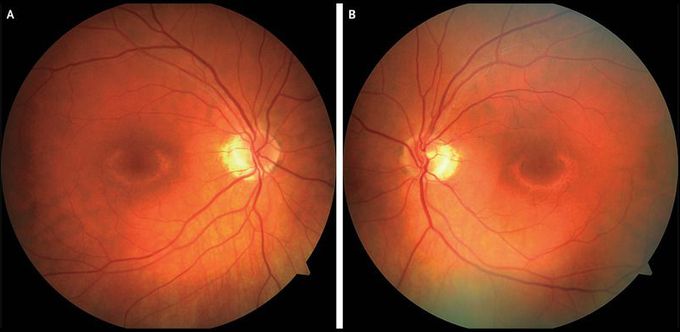
Bull’s-Eye Maculopathy Associated with Hydroxychloroquine
A 60-year-old woman presented to the ophthalmology clinic after noticing central blind spots in the visual fields of both eyes. She had a history of rheumatoid arthritis, which had been treated with hydroxychloroquine at a dose of 400 mg daily for 14 years. The visual acuity was 20/20 in both eyes. The retinal examination showed a bull’s-eye pattern of hypopigmentation in both the right eye (Panel A) and the left eye (Panel B). Visual-field testing showed ring scotomas, and retinal imaging on optical coherence tomography showed corresponding loss of photoreceptors and retinal pigment epithelium, findings that are consistent with hydroxychloroquine toxicity. Hydroxychloroquine was switched to methotrexate, and 6 months later, the patient’s ocular condition remained stable.

